Acute torsion of the gallbladder: a case report
- PMID: 20181172
- PMCID: PMC2827113
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1626-0002-0000006641
Acute torsion of the gallbladder: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Torsion of gallbladder is an uncommon cause of acute abdomen. Volvulus occurs along the long axis of the gallbladder mesentery, and according to the degree of rotation symptoms, and signs may vary.
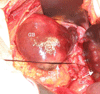
Case presentation: A 79-year-old woman presented with a one-day history of acute onset of right upper abdominal pain. The patient underwent laparotomy with a preoperative diagnosis of acalculous cholecystitis with possible gangrene. At laparotomy, the gallbladder was distended, and multiple necrotic areas were observed. It was rotated more than 180 degrees clockwise around the mesentery, and cholecystectomy was performed.
Conclusion: Cholecystectomy is the treatment of gallbladder torsion. Clinical signs and radiographic studies may be helpful to diagnose gallbladder torsion. Early diagnosis and surgical treatment lower the mortality of disease.
Figures

References
-
- Losken A, Wilson BW, Sherman R. Torsion of the gallbladder: a case report and review of the literature. Am Surg. 1997;63:975–978. - PubMed
-
- Kalimi R, Zarcone J III, McNellis J. Acute necrotizing torsion of the gallbladder. Am Surg. 2001;67:748–751. - PubMed
-
- Shaikh AA, Charles A, Domingo S, Schaub G. Gallbladder volvulus: report of two original cases and review of the literature. Am Surg. 2005;71:87–89. - PubMed
-
- Steiber AC, Bauer IJ. Volvulus of the gallbladder. Am J Gastroenterol. 1983;78:96–98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

