Coronin-1C is a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma invasive progression identified by proteomics analysis and clinical validation
- PMID: 20181269
- PMCID: PMC2845108
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-17
Coronin-1C is a novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma invasive progression identified by proteomics analysis and clinical validation
Abstract
Background: To better search for potential markers for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) invasion and metastasis, proteomic approach was applied to identify potential metastasis biomarkers associated with HCC.
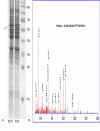
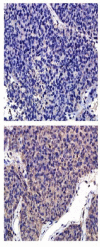
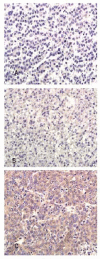
Methods: Membrane proteins were extracted from MHCC97L and HCCLM9 cells, with a similar genetic background and remarkably different metastasis potential, and compared by SDS-PAGE and identified by ESI-MS/MS. The results were further validated by western blot analysis, immunohistochemistry (IHC) of tumor tissues from HCCLM9- and MHCC97L-nude mice, and clinical specimens.
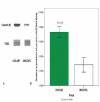
Results: Membrane proteins were extracted from MHCC97L and HCCLM9 cell and compared by SDS-PAGE analyses. A total of 14 differentially expressed proteins were identified by ESI-MS/MS. Coronin-1C, a promising candidate, was found to be overexpressed in HCCLM9 cells as compared with MHCC97L cells, and validated by western blot and IHC from both nude mice tumor tissues and clinical specimens. Coronin-1C level showed an abrupt upsurge when pulmonary metastasis occurred. Increasing coronin-1C expression was found in liver cancer tissues of HCCLM9-nude mice with spontaneous pulmonary metastasis. IHC study on human HCC specimens revealed that more patients in the higher coronin-1C group had overt larger tumor and more advanced stage.
Conclusions: Coronin-1C could be a candidate biomarker to predict HCC invasive behavior.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Increased coronin-1C expression is related to hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010 Jul;18(7):516-9. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2010.07.011. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20678442 Chinese.
-
Knockdown of Coronin-1C disrupts Rac1 activation and impairs tumorigenic potential in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2013 Mar;29(3):1066-72. doi: 10.3892/or.2012.2216. Epub 2012 Dec 28. Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23292607
-
Identification of an aptamer through whole cell-SELEX for targeting high metastatic liver cancers.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 16;7(7):8282-94. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6988. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26882565 Free PMC article.
-
From proteomic analysis to clinical significance: overexpression of cytokeratin 19 correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004 Jan;3(1):73-81. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M300094-MCP200. Epub 2003 Oct 30. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004. PMID: 14593079
-
FLNA and PGK1 are two potential markers for progression in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27(3-4):207-16. doi: 10.1159/000327946. Epub 2011 Apr 1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21471709
Cited by
-
CORO6 Promotes Cell Growth and Invasion of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma via Activation of WNT Signaling.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 May 7;9:647301. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.647301. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34026752 Free PMC article.
-
Coronin 1C inhibits melanoma metastasis through regulation of MT1-MMP-containing extracellular vesicle secretion.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 20;10(1):11958. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67465-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32686704 Free PMC article.
-
ACOX2 is a prognostic marker and impedes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via PPARα pathway.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jan 4;12(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03291-2. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33414412 Free PMC article.
-
Serum proteomic and metabolomic profiling of hepatocellular carcinoma patients co-infected with Clonorchis sinensis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1489077. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1489077. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39840062 Free PMC article.
-
CRN2 enhances the invasiveness of glioblastoma cells.Neuro Oncol. 2013 May;15(5):548-61. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nos388. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Neuro Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23410663 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sell S. Mouse Models to Study the Interaction of Risk Factors for Human Liver Cancer. Cancer Res. 2003;63:7553–7562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

