Histopathology and apoptosis in an animal model of reversible renal injury
- PMID: 20181466
- PMCID: PMC3951867
- DOI: 10.1016/j.etp.2010.02.002
Histopathology and apoptosis in an animal model of reversible renal injury
Abstract
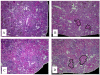
High adenine phosphate (HAP) diet serves as an animal model of chronic renal failure (RF). Induction of RF and establishment of end organ damage require long exposure periods to this diet. Previously, we have shown that RF is reversible after diet cessation even after protracted administration. In this study, we explored the underlying renal changes and cellular pathways occurring during administration and after cessation of the diet. Kidneys were obtained from rats fed HAP diet for 7 weeks, and from rats fed HAP diet followed a 10 week recovery period on normal diet. The kidneys of HAP diet group were significantly enlarged due to tubular injury characterized by massive cystic dilatation and crystal deposition. Kidney injury was associated with markers of apoptosis as well as with activation of apoptosis related pathways. Diet cessation was associated with a significant reduction in kidney size, tubules diameter, and crystals deposition. The recovery from renal injury was coupled with regression of apoptotic features. This is the first study showing the potential reversibility of long standing RF model, allowing optimal evaluation of uremia-chronic effects.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Thalidomide suppresses inflammation in adenine-induced CKD with uraemia in mice.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013 May;28(5):1140-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs569. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2013. PMID: 23345625
-
Augmenter of liver regeneration attenuates tubular cell apoptosis in acute kidney injury in rats: the possible mechanisms.Ren Fail. 2012;34(5):590-9. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2012.664470. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Ren Fail. 2012. PMID: 22417144
-
Limitation of apoptotic changes in renal tubular cell injury induced by hyperoxaluria.Urol Res. 2004 Aug;32(4):271-7. doi: 10.1007/s00240-003-0393-3. Epub 2004 Jul 13. Urol Res. 2004. PMID: 15249986
-
Functional and histological effects of Anthurium schlechtendalii Kunth extracts on adenine-induced kidney damage of adult Wistar rats.Toxicon. 2023 Sep;233:107272. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2023.107272. Epub 2023 Aug 29. Toxicon. 2023. PMID: 37652102 Review.
-
Hypoxic preconditioning reinforces HIF-alpha-dependent HSP70 signaling to reduce ischemic renal failure-induced renal tubular apoptosis and autophagy.Life Sci. 2010 Jan 16;86(3-4):115-23. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2009.11.022. Epub 2009 Dec 4. Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 19962996
Cited by
-
Raloxifene attenuates Gas6 and apoptosis in experimental aortic valve disease in renal failure.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):H1829-40. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00240.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21335463 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium copper chlorophyllin attenuates adenine-induced chronic kidney disease via suppression of TGF-beta and inflammatory cytokines.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Nov;393(11):2029-2041. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01912-3. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32500189
-
Protective potential of curcumin in L-NAME-induced hypertensive rat model: AT1R, mitochondrial DNA synergy.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2020 Oct 15;12(5):134-146. eCollection 2020. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33224436 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol-Lowering Action of a Novel Nutraceutical Combination in Uremic Rats: Insights into the Molecular Mechanism in a Hepatoma Cell Line.Nutrients. 2020 Feb 9;12(2):436. doi: 10.3390/nu12020436. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32050453 Free PMC article.
-
Intermittent hypoxia exacerbates increased blood pressure in rats with chronic kidney disease.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Oct 1;315(4):F927-F941. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00420.2017. Epub 2018 Jun 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29897288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum J, Mehta R, Palevsky P, The ADQI workgroup Acute renal failure – definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Critical Care. 2004;8:R204–12. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ben-Sasson S, Sherman Y, Gavrieli Y. Identification of dying cells – in situ staining. Methods Cell Biol. 1995;46:29–39. - PubMed
-
- Go A, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu C. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:1296–305. - PubMed
-
- Heyman SN, Rosen S, Darmon D, Goldfarb M, Bitz H, Shina A, et al. Endotoxin-induced renal failure: II. A role for tubular hypoxic damage. Exp Nephrol. 2000;8:275–82. - PubMed
-
- Katsumata K, Kenichiro K, Michinori H, Kunihiko T, Nobuo N, Steven KB, et al. Sevelamer hydrochloride prevents ectopic calcification and renal osteodystrophy in chronic renal failure rats. Kidney Int. 2003;64:441–50. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

