Organization and physiology of posterior lateral line afferent neurons in larval zebrafish
- PMID: 20181553
- PMCID: PMC2880066
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2009.0995
Organization and physiology of posterior lateral line afferent neurons in larval zebrafish
Abstract
The lateral line system of larval zebrafish can translate hydrodynamic signals from the environment to guide body movements. Here, I demonstrate a spatial relationship between the organization of afferent neurons in the lateral line ganglion and the innervation of neuromasts along the body. I developed a whole cell patch clamp recording technique to show that afferents innervate multiple direction-sensitive neuromasts, which are sensitive to low fluid velocities. This work lays the foundation to integrate sensory neuroscience and the hydrodynamics of locomotion in a model genetic system.
Figures
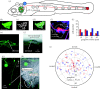

References
-
- Alexandre D., Ghysen A.1999Somatotopy of the lateral line projection in larval zebrafish. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7558–7562 (doi:10.1073/pnas.96.13.7558) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Catton K. B., Webster D. R., Brown J., Yen J.2007Quantitative analysis of tethered and free-swimming copepodid flow fields. J. Exp. Biol. 210, 299–310 (doi:10.1242/jeb.02633) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chagnaud B. P., Bleckmann H., Engelmann J.2006Neural responses of goldfish lateral line afferents to vortex motions. J. Exp. Biol. 209, 327–342 (doi:10.1242/jeb.01982) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coombs S., Conley R. A.1997Dipole source localization by mottled sculpin. I. Approach strategies. J. Comp. Physiol. A 180, 387–399 (doi:10.1007/s003590050057) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coombs S., Montgomery J. C.1992Fibers innervating different parts of the lateral line system of the Antarctic fish, Trematomus bernacchii, have similar neural responses despite large variations in peripheral morphology. Brain Behav. Evol. 40, 217–233 (doi:10.1159/000113914) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
