The blood parasite Haemoproteus reduces survival in a wild bird: a medication experiment
- PMID: 20181556
- PMCID: PMC2936130
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2010.0046
The blood parasite Haemoproteus reduces survival in a wild bird: a medication experiment
Abstract
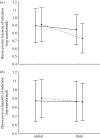
While avian chronic haemoparasite infections induce reproductive costs, infection has not previously been shown to affect survival. Here, we experimentally reduced, through medication, the intensity of infection by Haemoproteus parasites in wild-breeding female blue tits Cyanistes caeruleus. However, this treatment did not reduce the intensity of infection in males or the intensity of infection by Leucocytozoon. Medicated females, but not males, showed increased local survival until the next breeding season compared with control birds. To our knowledge, this is the first empirical evidence showing long-term direct survival costs of chronic Haemoproteus infections in wild birds.
Figures
References
-
- de Lope F., Møller A. P., Cruz C.1998Parasitism, immune response and reproductive success in the house martin Delichon urbica. Oecologia 114, 188–193 (doi:10.1007/s004420050435) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dimitrova D., Moutafchieva R., Kanelov I., Dinev T., Lashev L.2009Pharmacokinetics of tobramycin in ducks and sex-related differences. Vet. J. 179, 462–464 (doi:10.1016/j.tvjl.2007.10.003) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gordi T., Huong D. X., Hai T. N., Nieu N. T., Ashton M.2002Artemisinin pharmacokinetics and efficacy in uncomplicated-malaria patients treated with two different dosage regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 46, 1026–1031 (doi:10.1128/AAC.46.4.1026-1031.2002) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hanssen S. A., Folstad I., Erikstad K. E., Oksanen A.2003Cost of parasites in common eiders: effects of antiparasite treatment. Oikos 100, 105–111 (doi:10.1034/j.1600-0706.2003.12162.x) - DOI
-
- Hudson P. J., Dobson A. P.1991The direct and indirect effects of the caecal nematode Trichostrongylus tenuis on red grouse. In Bird–parasite interactions: ecology, evolution and behaviour (ed. Loye J. E.), pp. 49–68 Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

