Interaction between Ephrins and mGlu5 metabotropic glutamate receptors in the induction of long-term synaptic depression in the hippocampus
- PMID: 20181581
- PMCID: PMC6633947
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4834-09.2010
Interaction between Ephrins and mGlu5 metabotropic glutamate receptors in the induction of long-term synaptic depression in the hippocampus
Abstract
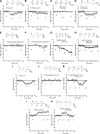
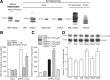
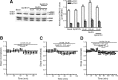
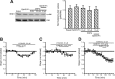
We applied the group-I metabotropic glutamate (mGlu) receptor agonist, 3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine (DHPG), to neonatal or adult rat hippocampal slices at concentrations (10 microM) that induced a short-term depression (STD) of excitatory synaptic transmission at the Schaffer collateral/CA1 synapses. DHPG-induced STD was entirely mediated by the activation of mGlu5 receptors because it was abrogated by the mGlu5 receptor antagonist, MPEP [2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)pyridine], but not by the mGlu1 receptor antagonist, CPCCOEt [7-(hydroxyimino)cyclopropa[b]chromen-1a-carboxylate ethyl ester]. Knowing that ephrin-Bs functionally interact with group-I mGlu receptors (Calò et al., 2005), we examined whether pharmacological activation of ephrin-Bs could affect DHPG-induced STD. We activated ephrin-Bs using their cognate receptor, EphB1, under the form of a preclustered EphB1/Fc chimera. Addition of clustered EphB1/Fc alone to the slices induced a small but nondecremental depression of excitatory synaptic transmission, which differed from the depression induced by 10 microM DHPG. Surprisingly, EphB1/Fc-induced synaptic depression was abolished by MPEP (but not by CPCCOEt) suggesting that it required the endogenous activation of mGlu5 receptors. In addition, coapplication of DHPG and EphB1/Fc, resulted in a large and nondecremental long-term depression. The effect of clustered EphB1/Fc was specific because it was not mimicked by unclustered EphB1/Fc or clustered EphA1/Fc. These findings raise the intriguing possibility that changes in synaptic efficacy mediated by mGlu5 receptors are under the control of the ephrin/Eph receptor system, and that the neuronal actions of ephrins can be targeted by drugs that attenuate mGlu5 receptor signaling.
Figures

References
-
- Ango F, Prézeau L, Muller T, Tu JC, Xiao B, Worley PF, Pin JP, Bockaert J, Fagni L. Agonist-independent activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors by the intracellular protein Homer. Nature. 2001;41:962–965. - PubMed
-
- Anwyl R. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: electrophysiological properties and role in plasticity. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1999;29:83–120. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Busceti CL, Molinaro G, Biagioni F, Storto M, Fornai F, Nicoletti F, Bruno V. Endogenous activation of mGlu5 metabotropic glutamate receptors contributes to the development of nigro-striatal damage induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine in mice. J Neurosci. 2004;28:828–835. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
