Proteomic identification of binding partners for the brain metabolite lanthionine ketimine (LK) and documentation of LK effects on microglia and motoneuron cell cultures
- PMID: 20181595
- PMCID: PMC2836831
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5247-09.2010
Proteomic identification of binding partners for the brain metabolite lanthionine ketimine (LK) and documentation of LK effects on microglia and motoneuron cell cultures
Abstract
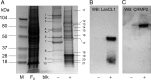
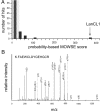
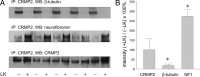
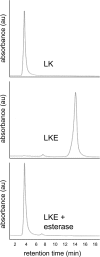
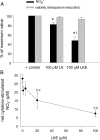
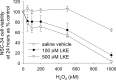
Lanthionine ketimine (LK) represents a poorly understood class of thioethers present in mammalian CNS. Previous work has indicated high-affinity interaction of LK with synaptosomal membrane protein(s), but neither LK binding partners nor specific bioactivities have been reported. In this study, LK was chemically synthesized and used as an affinity agent to capture binding partners from mammalian brain lysate. Liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry of electrophoretically separated, LK-bound proteins identified polypeptides implicated in axon remodeling or vesicle trafficking and diseases including Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia: collapsin response mediator protein-2/dihydropyrimidinase-like protein-2 (CRMP2/DRP2/DPYSL2), myelin basic protein, and syntaxin-binding protein-1 (STXBP1/Munc-18). Also identified was the recently discovered glutathione-binding protein lanthionine synthetase-like protein-1. Functional consequences of LK:CRMP2 interactions were probed through immunoprecipitation studies using brain lysate wherein LK was found to increase CRMP2 coprecipitation with its partner neurofibromin-1 but decreased CRMP2 coprecipitation with beta-tubulin. Functional studies of NSC-34 motor neuron-like cells indicated that a cell-permeable LK-ester, LKE, was nontoxic and protective against oxidative challenge with H(2)O(2). LKE-treated NSC-34 cells significantly increased neurite number and length in a serum concentration-dependent manner, consistent with a CRMP2 interaction. Finally, LKE antagonized the activation of EOC-20 microglia by inflammogens. The results are discussed with reference to possible biochemical origins, paracrine functions, neurological significance, and pharmacological potential of lanthionyl compounds.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A cell-penetrating ester of the neural metabolite lanthionine ketimine stimulates autophagy through the mTORC1 pathway: Evidence for a mechanism of action with pharmacological implications for neurodegenerative pathologies.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Dec;84:60-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25779968 Free PMC article.
-
Lanthionine ketimine ethyl ester partially rescues neurodevelopmental defects in unc-33 (DPYSL2/CRMP2) mutants.J Neurosci Res. 2013 Sep;91(9):1183-90. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23239. Epub 2013 Jul 3. J Neurosci Res. 2013. PMID: 23825043
-
Lanthionine ketimine ester provides benefit in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.J Neurochem. 2015 Jul;134(2):302-14. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13114. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25846048
-
The protein interactome of collapsin response mediator protein-2 (CRMP2/DPYSL2) reveals novel partner proteins in brain tissue.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2015 Oct;9(9-10):817-31. doi: 10.1002/prca.201500004. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2015. PMID: 25921334 Review.
-
Collapsin response mediator protein-2: an emerging pathologic feature and therapeutic target for neurodisease indications.Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Jun;43(3):180-91. doi: 10.1007/s12035-011-8166-4. Epub 2011 Jan 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2011. PMID: 21271304 Review.
Cited by
-
Opening Pandora's jar: a primer on the putative roles of CRMP2 in a panoply of neurodegenerative, sensory and motor neuron, and central disorders.Future Neurol. 2012 Nov 1;7(6):749-771. doi: 10.2217/FNL.12.68. Future Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23308041 Free PMC article.
-
CRMPs Function in Neurons and Glial Cells: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Neurodegenerative Diseases and CNS Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Aug;54(6):4243-4256. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0005-1. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27339876 Review.
-
Lanthionine synthetase C-like protein 1 interacts with and inhibits cystathionine β-synthase: a target for neuronal antioxidant defense.J Biol Chem. 2012 Oct 5;287(41):34189-201. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.383646. Epub 2012 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22891245 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic inhibition of CRMP2 phosphorylation at serine 522 promotes axonal regeneration after optic nerve injury.Sci Rep. 2019 May 10;9(1):7188. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43658-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31076621 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-penetrating ester of the neural metabolite lanthionine ketimine stimulates autophagy through the mTORC1 pathway: Evidence for a mechanism of action with pharmacological implications for neurodegenerative pathologies.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Dec;84:60-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.03.007. Epub 2015 Mar 14. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25779968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberg K, Axelsson E, Saetre P, Jiang L, Wetterberg L, Pettersson U, Lindholm E, Jazin E. Support for schizophrenia susceptibility locus on chromosome 2q detected in a Swedish isolate using a dense map of microsatellites and SNPs. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2008;147B:1238–1244. - PubMed
-
- Arimura N, Inagaki N, Chihara K, Menager C, Nakamura N, Iwamatsu A. Phosphorylation of CRMP-2 by Rho kinase: evidence for two separate signaling pathways for growth cone collapse. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:23,973–23:980. - PubMed
-
- Arimura N, Menager C, Fukata Y, Kaibuchi K. Role of CRMP-2 in neuronal polarity. J Neurobiol. 2004;58:34–47. - PubMed
-
- Behan AT, Byrne C, Dunn MJ, Cagney G, Cotter DR. Proteomic analysis of membrane microdomain-associated proteins in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder reveals alterations in LAMP, STXBP1 and BASP1 protein expression. Mol Psychiatry. 2009;14:601–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
