Unique contributions of distinct cholinergic projections to motor cortical plasticity and learning
- PMID: 20181623
- PMCID: PMC2951849
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhq022
Unique contributions of distinct cholinergic projections to motor cortical plasticity and learning
Abstract
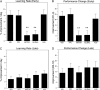
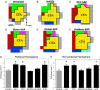
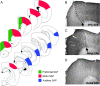
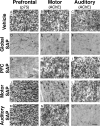
The cholinergic basal forebrain projects throughout the neocortex, exerting a critical role in modulating plasticity associated with normal learning. Cholinergic modulation of cortical plasticity could arise from 3 distinct mechanisms by 1) "direct" modulation via cholinergic inputs to regions undergoing plasticity, 2) "indirect" modulation via cholinergic projections to anterior, prefrontal attentional systems, or 3) modulating more global aspects of processing via distributed inputs throughout the cortex. To segregate these potential mechanisms, we investigated cholinergic-dependent reorganization of cortical motor representations in rats undergoing skilled motor learning. Behavioral and electrophysiological consequences of depleting cholinergic inputs to either motor cortex, prefrontal cortex, or globally, were compared. We find that local depletion of cholinergic afferents to motor cortex significantly disrupts map plasticity and skilled motor behavior, whereas prefrontal cholinergic depletion has no effect on these measures. Global cholinergic depletion perturbs map plasticity comparable with motor cortex depletions but results in significantly greater impairments in skilled motor acquisition. These findings indicate that local cholinergic activation within motor cortex, as opposed to indirect regulation of prefrontal systems, modulate cortical map plasticity and motor learning. More globally acting cholinergic mechanisms provide additional support for the acquisition of skilled motor behaviors, beyond those associated with cortical map reorganization.
Figures

References
-
- Baskerville KA, Schweitzer JB, Herron P. Effects of cholinergic depletion on experience-dependent plascticity in the cortex of the rat. Neuroscience. 1997;80(4):1159–1169. - PubMed
-
- Bjordahl TS, Dimyan MA, Weinberger NM. Induction of long-term receptive field plasticity in the auditory cortex of the waking guinea pig by stimulation of the nucleus basalis. Behav Neurosci. 1998;112:467–479. - PubMed

