Hematopoietic cell kinase associates with the 40S ribosomal subunit and mediates the ribotoxic stress response to deoxynivalenol in mononuclear phagocytes
- PMID: 20181660
- PMCID: PMC2902856
- DOI: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq055
Hematopoietic cell kinase associates with the 40S ribosomal subunit and mediates the ribotoxic stress response to deoxynivalenol in mononuclear phagocytes
Abstract
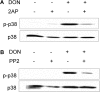
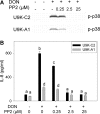
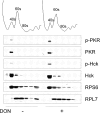
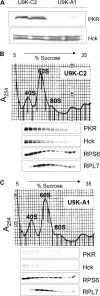
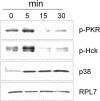
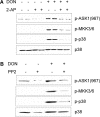
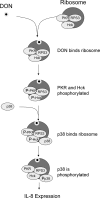
The trichothecene deoxynivalenol (DON) binds to eukaryotic ribosomes and triggers p38-driven proinflammatory gene expression in the macrophage-a response that is dependent on both double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase (PKR) and hematopoietic cell kinase (Hck). Here we elucidated critical linkages that exist among the ribosome and these kinases during the course of DON-induced ribotoxic stress in mononuclear phagocytes. Similar to PKR inhibitors, Hck inhibitor 4-amino-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-7-(t-butyl)pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyramidine (PP2) suppressed p38 activation and p38-driven interleukin 8 (IL-8) expression in the U937 human monocyte cell line. U937 cells stably transfected with a PKR antisense vector (U9K-A1) displayed marked reduction of DON-induced p38 activation and IL-8 expression as compared to cells transfected with empty vector (U9K-C2), with both responses being completely ablated by PP2. Western analysis of sucrose density gradient fractions revealed that PKR and Hck interacted with the 40S ribosomal subunit in U9K-C2 but not U9K-A1 cells. Subsequent transfection and immunoprecipitation studies with HeLa cells indicated that Hck interacted with ribosomal protein S3. Consistent with U937 cells, DON induced p38 association with the ribosome and phosphorylation in peritoneal macrophages from wild-type but not PKR-deficient mice. DON-induced phosphorylation of ribosome-associated Hck in RAW 264.7 murine macrophages was also suppressed by 2-aminopurine (2-AP). Both 2-AP and PP2 inhibited DON-induced phosphorylation of p38 as well as two kinases, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase 3/6, known to be upstream of p38. Taken together, PKR and Hck were critical for DON-induced ribosomal recruitment of p38, its subsequent phosphorylation, and, ultimately, p38-driven proinflammatory cytokine expression.
Figures


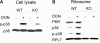

References
-
- Arold ST, Ulmer TS, Mulhern TD, Werner JM, Ladbury JE, Campbell ID, Noble ME. The role of the Src homology 3-Src homology 2 interface in the regulation of Src kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:17199–17205. - PubMed
-
- Balachandran S, Barber GN. PKR in innate immunity, cancer, and viral oncolysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007;383:277–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

