Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms, pathologic consequences, and potential for therapeutic manipulation
- PMID: 20182045
- PMCID: PMC3792565
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1414
Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: mechanisms, pathologic consequences, and potential for therapeutic manipulation
Abstract
The concept of neuroinflammation has evolved over the past two decades from an initially controversial viewpoint to its present status as a generally accepted idea whose mechanisms and consequences are still actively under research and debate, particularly with regard to Alzheimer's disease (AD). This review summarizes the current status of neuroinflammation research as it specifically relates to AD. Neuroinflammation is discussed mechanistically with emphasis on the role of redox signal transduction linked to the activation of central nervous system-relevant innate immune pathways. Redox signaling is presented both as a causal factor and a consequence of sustained neuroinflammation. Functional relationships are discussed that connect distinct neuroinflammatory components such as cytokines, eicosanoids, classic AD pathology (amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles), and the recently emergent notion of "damage-associated molecular patterns". The interaction of these paracrine factors likely can produce positive as well as negative effects on the AD brain, ranging from plaque clearance by microglia in the short term to glial dysfunction and neuronal compromise if the neuroinflammation is chronically sustained and unmitigated. Recent disappointments in AD clinical trials of anti-inflammatory drugs are discussed with reference to possible explanations and potential avenues for future pharmacological approaches to the disease.
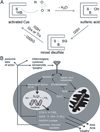
Figures
References
-
- McGeer PL, Rogers J, McGeer EG, Sibley J. Anti-inflammatory drugs and Alzheimer’s disease? Lancet. 1990;335:1037. - PubMed
-
- Rogers J. The inflammatory response in Alzheimer’s disease. J Periodontol. 2008;79:1535–1543. - PubMed
-
- McGeer PL, McGeer EG. NSAIDs and Alzheimer disease: Epidemiological, animal model and clinical studies. Neumbiol Aging. 2007;88:639–647. - PubMed
-
- McGeer PL, Schulzer M, McGeer EG. Arthritis and anti-inflammatory agents as possible protective factors for Alzheimer’s disease: A review of 17 epidemiologic studies. Neurology. 1996;47:425–432. - PubMed
-
- In’t Veld BA, Ruitenberg A, Hofman A, Launer LJ, vn Duijn CM, Stijnen T, Breteler MM, Strieker BH. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:1515–1521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

