Identification of pancreas-specific proteins in endoscopically (endoscopic pancreatic function test) collected pancreatic fluid with liquid chromatography--tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 20182389
- PMCID: PMC2891328
- DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181cf16f4
Identification of pancreas-specific proteins in endoscopically (endoscopic pancreatic function test) collected pancreatic fluid with liquid chromatography--tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to establish the endoscopic pancreatic function test (ePFT) as a method that can safely obtain pancreatic fluid for mass spectrometric analysis from patients during upper endoscopy and to reproducibly identify pancreas-specific proteins.
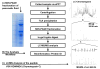
Methods: We performed a sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry-based proteomic analysis (in-gel tryptic digestion followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry [GeLC-MS/MS]) on ePFT-collected pancreatic fluid from 3 individuals, without evidence of chronic pancreatitis, who were undergoing an upper endoscopy for dyspepsia and chronic abdominal pain.
Results: Pancreatic fluid was safely collected from all subjects. The sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of ePFT-collected pancreatic fluid revealed no significant variation (F statistic, 1.33, P = 0.29) in protein concentration during the 1-hour collection period and a visually reproducible protein banding pattern among the 3 subjects. The GeLC-MS/MS analysis of ePFT-collected fluid identified pancreas-specific proteins previously described from endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and surgical collection methods. Gene ontology further revealed that most of the proteins identified have a molecular function of proteases.
Conclusions: The ePFT is capable of collecting large amounts of pancreatic fluid for proteomic analysis enabling the identification of pancreas-specific proteins. This endoscopic collection method coupled with GeLC-MS/MS is a powerful technique, which can be used in future investigations to elucidate pathways involved in the development and progression of pancreatic disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Difference gel electrophoresis identifies differentially expressed proteins in endoscopically collected pancreatic fluid.Electrophoresis. 2011 Aug;32(15):1939-51. doi: 10.1002/elps.201100203. Electrophoresis. 2011. PMID: 21792986 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics of endoscopically collected pancreatic fluid in chronic pancreatitis research.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011 Apr;5(3-4):109-20. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000098. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011. PMID: 21360826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of endoscopically (endoscopic pancreatic function test) collected gastroduodenal fluid using in-gel tryptic digestion followed by LC-MS/MS.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2010 Sep;4(8-9):715-25. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000018. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2010. PMID: 21137089 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of endoscopic pancreatic function test (ePFT)-collected pancreatic fluid proteins precipitated via ultracentrifugation.JOP. 2013 Mar 10;14(2):176-86. doi: 10.6092/1590-8577/1272. JOP. 2013. PMID: 23474565 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Pancreas Fluid Collection: Methods and Relevance for Clinical Care and Translational Science.Am J Gastroenterol. 2016 Sep;111(9):1258-66. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.297. Epub 2016 Aug 2. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27481304 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differentiating Branch Duct and Mixed IPMN in Endoscopically Collected Pancreatic Cyst Fluid via Cytokine Analysis.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012;2012:247309. doi: 10.1155/2012/247309. Epub 2012 Dec 25. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2012. PMID: 23326260 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of in-gel protein separation techniques commonly used for fractionation in mass spectrometry-based proteomic profiling.Electrophoresis. 2012 Aug;33(16):2516-26. doi: 10.1002/elps.201200031. Electrophoresis. 2012. PMID: 22899259 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic analysis (GeLC-MS/MS) of ePFT-collected pancreatic fluid in chronic pancreatitis.J Proteome Res. 2012 Mar 2;11(3):1897-912. doi: 10.1021/pr2011022. Epub 2012 Feb 7. J Proteome Res. 2012. PMID: 22243521 Free PMC article.
-
Difference gel electrophoresis identifies differentially expressed proteins in endoscopically collected pancreatic fluid.Electrophoresis. 2011 Aug;32(15):1939-51. doi: 10.1002/elps.201100203. Electrophoresis. 2011. PMID: 21792986 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometry-based proteomics of endoscopically collected pancreatic fluid in chronic pancreatitis research.Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011 Apr;5(3-4):109-20. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000098. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011. PMID: 21360826 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Thongboonkerd V. Proteomics of human body fluids : principles, methods, and applications. Totowa, N.J.: Humana Press; 2007. p. xiii.p. 533.
-
- Anderson NL, Polanski M, Pieper R, et al. The human plasma proteome: a nonredundant list developed by combination of four separate sources. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2004;3(4):311–26. - PubMed
-
- Gronborg M, Bunkenborg J, Kristiansen TZ, et al. Comprehensive proteomic analysis of human pancreatic juice. J Proteome Res. 2004;3(5):1042–55. - PubMed
-
- Muthusamy B, Hanumanthu G, Suresh S, et al. Plasma Proteome Database as a resource for proteomics research. Proteomics. 2005;5(13):3531–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

