An essential role for XBP-1 in host protection against immune activation in C. elegans
- PMID: 20182512
- PMCID: PMC2834299
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08762
An essential role for XBP-1 in host protection against immune activation in C. elegans
Abstract
The detection and compensatory response to the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), termed the unfolded protein response (UPR), represents a conserved cellular homeostatic mechanism with important roles in normal development and in the pathogenesis of disease. The IRE1-XBP1/Hac1 pathway is a major branch of the UPR that has been conserved from yeast to human. X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) is required for the differentiation of the highly secretory plasma cells of the mammalian adaptive immune system, but recent work also points to reciprocal interactions between the UPR and other aspects of immunity and inflammation. We have been studying innate immunity in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, having established a principal role for a conserved PMK-1 p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in mediating resistance to microbial pathogens. Here we show that during C. elegans development, XBP-1 has an essential role in protecting the host during activation of innate immunity. Activation of the PMK-1-mediated response to infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa induces the XBP-1-dependent UPR. Whereas a loss-of-function xbp-1 mutant develops normally in the presence of relatively non-pathogenic bacteria, infection of the xbp-1 mutant with P. aeruginosa leads to disruption of ER morphology and larval lethality. Unexpectedly, the larval lethality phenotype on pathogenic P. aeruginosa is suppressed by loss of PMK-1-mediated immunity. Furthermore, hyperactivation of PMK-1 causes larval lethality in the xbp-1 mutant even in the absence of pathogenic bacteria. Our data establish innate immunity as a physiologically relevant inducer of ER stress during C. elegans development and indicate that an ancient, conserved role for XBP-1 may be to protect the host organism from the detrimental effects of mounting an innate immune response to microbes.
Figures
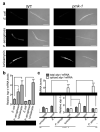
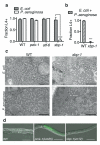
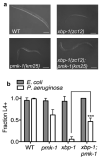
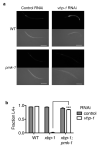
Comment in
-
Survive an innate immune response through XBP1.Cell Res. 2010 May;20(5):506-7. doi: 10.1038/cr.2010.61. Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 20436510 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Organismal regulation of XBP-1-mediated unfolded protein response during development and immune activation.EMBO Rep. 2012 Sep;13(9):855-60. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.100. Epub 2012 Jul 13. EMBO Rep. 2012. PMID: 22791024 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis Is Modulated by the Forkhead Transcription Factor FKH-9 During Infection of Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2018 Dec;210(4):1329-1337. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301450. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 30287474 Free PMC article.
-
Dioscin Activates Endoplasmic Reticulum Unfolded Protein Response for Defense Against Pathogenic Bacteria in Caenorhabditis elegans via IRE-1/XBP-1 Pathway.J Infect Dis. 2024 Jan 12;229(1):237-244. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad294. J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 37499184
-
Local and long-range activation of innate immunity by infection and damage in C. elegans.Curr Opin Immunol. 2016 Feb;38:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Oct 28. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26517153 Review.
-
Insights from the worm: the C. elegans model for innate immunity.Semin Immunol. 2014 Aug;26(4):303-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 May 21. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24856329 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disease tolerance as a defense strategy.Science. 2012 Feb 24;335(6071):936-41. doi: 10.1126/science.1214935. Science. 2012. PMID: 22363001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pig immune response to general stimulus and to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection: a meta-analysis approach.BMC Genomics. 2013 Apr 3;14:220. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-220. BMC Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23552196 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-extrinsic effects of tumor ER stress imprint myeloid dendritic cells and impair CD8⁺ T cell priming.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51845. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051845. Epub 2012 Dec 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23272178 Free PMC article.
-
Caenorhabditis elegans microRNAs of the let-7 family act in innate immune response circuits and confer robust developmental timing against pathogen stress.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 5;112(18):E2366-75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422858112. Epub 2015 Apr 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25897023 Free PMC article.
-
Sugar restriction and blood ingestion shape divergent immune defense trajectories in the mosquito Aedes aegypti.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 31;13(1):12368. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39067-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37524824 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schröder M, Kaufman RJ. The mammalian Unfolded Protein Response. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005;74:739–789. - PubMed
-
- Cox JS, Walter P. A novel mechanism for regulating activity of a transcription factor that controls the Unfolded Protein Response. Cell. 1996;87:391–404. - PubMed
-
- Mori K, Kawahara T, Yoshida H, Yanagi H, Yura T. Signalling from Endoplasmic Reticulum to nucleus: transcription factor with a basic-leucine zipper motif is required for the Unfolded Protein Response pathway. Genes Cells. 1996;1:803–817. - PubMed
-
- Shen X, et al. Complementary signaling pathways regulate the Unfolded Protein Response and are required for C. elegans development. Cell. 2001;107:893–903. - PubMed
-
- Calfon M, et al. IRE1 couples endoplasmic reticulum load to secretory capacity by processing the xbp-1 mRNA. Nature. 2002;415:92–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

