Mediators of inflammation in acute kidney injury
- PMID: 20182538
- PMCID: PMC2825552
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/137072
Mediators of inflammation in acute kidney injury
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) remains to be an independent risk factor for mortality and morbidity. Inflammation is now believed to play a major role in the pathophysiology of AKI. It is hypothesized that in ischemia, sepsis and nephrotoxic models that the initial insult results in morphological and/or functional changes in vascular endothelial cells and/or in tubular epithelium. Then, leukocytes including neutrophils, macrophages, natural killer cells, and lymphocytes infiltrate into the injured kidneys. The injury induces the generation of inflammatory mediators like cytokines and chemokines by tubular and endothelial cells which contribute to the recruiting of leukocytes into the kidneys. Thus, inflammation has an important role in the initiation and extension phases of AKI. This review will focus on the mediators of inflammation contributing to the pathogenesis of AKI.
Figures
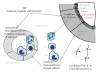
References
-
- Lameire N, Van Biesen W, Vanholder R. The changing epidemiology of acute renal failure. Nature Clinical Practice Nephrology. 2006;2(7):364–377. - PubMed
-
- Esson ML, Schrier RW. Diagnosis and treatment of acute tubular necrosis. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2002;137(9):744–752. - PubMed
-
- Liano F, Junco E, Pascual J, Madero R, Verde E. The spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit compared with that seen in other settings. The Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group. Kidney International, Supplement. 1998;66:S16–S24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

