Tight junctions in salivary epithelium
- PMID: 20182541
- PMCID: PMC2825559
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/278948
Tight junctions in salivary epithelium
Abstract
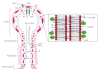
Epithelial cell tight junctions (TJs) consist of a narrow belt-like structure in the apical region of the lateral plasma membrane that circumferentially binds each cell to its neighbor. TJs are found in tissues that are involved in polarized secretions, absorption functions, and maintaining barriers between blood and interstitial fluids. The morphology, permeability, and ion selectivity of TJ vary among different types of tissues and species. TJs are very dynamic structures that assemble, grow, reorganize, and disassemble during physiological or pathological events. Several studies have indicated the active role of TJ in intestinal, renal, and airway epithelial function; however, the functional significance of TJ in salivary gland epithelium is poorly understood. Interactions between different combinations of the TJ family (each with their own unique regulatory proteins) define tissue specificity and functions during physiopathological processes; however, these interaction patterns have not been studied in salivary glands. The purpose of this review is to analyze some of the current data regarding the regulatory components of the TJ that could potentially affect cellular functions of the salivary epithelium.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Constitutive activation of Rho proteins by CNF-1 influences tight junction structure and epithelial barrier function.J Cell Sci. 2003 Feb 15;116(Pt 4):725-42. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00300. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12538773
-
Interferon-gamma increased epithelial barrier function via upregulating claudin-7 expression in human submandibular gland duct epithelium.J Mol Histol. 2016 Jun;47(3):353-63. doi: 10.1007/s10735-016-9667-2. Epub 2016 Mar 8. J Mol Histol. 2016. PMID: 26956365
-
Distribution of tight junction proteins in adult human salivary glands.J Histochem Cytochem. 2008 Dec;56(12):1093-8. doi: 10.1369/jhc.2008.951780. Epub 2008 Sep 2. J Histochem Cytochem. 2008. PMID: 18765838 Free PMC article.
-
Possible involvement of tight junctions, extracellular matrix and nuclear receptors in epithelial differentiation.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:253048. doi: 10.1155/2011/253048. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22162632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular basis of the core structure of tight junctions.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Jan;2(1):a002907. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002907. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20182608 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Encapsulation of Primary Salivary Gland Acinar Cell Clusters and Intercalated Ducts (AIDUCs) within Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-Degradable Hydrogels to Maintain Tissue Structure and Function.Adv Healthc Mater. 2022 Apr;11(7):e2101948. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202101948. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022. PMID: 34994104 Free PMC article.
-
Current trends in salivary gland tight junctions.Tissue Barriers. 2016 Mar 10;4(3):e1162348. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2016.1162348. eCollection 2016 Jul-Sep. Tissue Barriers. 2016. PMID: 27583188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell culture models of oral mucosal barriers: A review with a focus on applications, culture conditions and barrier properties.Tissue Barriers. 2018;6(3):1479568. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2018.1479568. Epub 2018 Sep 25. Tissue Barriers. 2018. PMID: 30252599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matriptase deletion initiates a Sjögren's syndrome-like disease in mice.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 13;9(2):e82852. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082852. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24551030 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of tricellular tight junction tricellulin leads to hyposalivation in Sjögren's syndrome.Int J Oral Sci. 2025 Mar 19;17(1):22. doi: 10.1038/s41368-025-00349-9. Int J Oral Sci. 2025. PMID: 40108118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sasaki H. Freeze-fracture analysis of renal-epithelial tight junctions. Methods in Molecular Medicine. 2003;86:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Nagafuchi A. Molecular architecture of adherens junctions. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2001;13(5):600–603. - PubMed
-
- Green KJ, Jones JCR. Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes: structure and function of molecular components. The FASEB Journal. 1996;10(8):871–881. - PubMed
-
- Lourenço SV, Kapas S. Integrin expression in developing human salivary glands. Histochemistry and Cell Biology. 2005;124(5):391–399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
