Synchronization of chromosome dynamics and cell division in bacteria
- PMID: 20182599
- PMCID: PMC2827906
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000331
Synchronization of chromosome dynamics and cell division in bacteria
Abstract
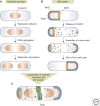
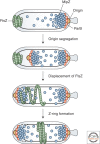
Bacterial cells have evolved a variety of regulatory circuits that tightly synchronize their chromosome replication and cell division cycles, thereby ensuring faithful transmission of genetic information to their offspring. Complex multicomponent signaling cascades are used to monitor the progress of cytokinesis and couple replication initiation to the separation of the two daughter cells. Moreover, the cell-division apparatus actively participates in chromosome partitioning and, particularly, in the resolution of topological problems that impede the segregation process, thus coordinating chromosome dynamics with cell constriction. Finally, bacteria have developed mechanisms that harness the cell-cycle-dependent positioning of individual chromosomal loci or the nucleoid to define the cell-division site and control the timing of divisome assembly. Each of these systems manages to integrate a complex set of spatial and temporal cues to regulate and execute critical steps in the bacterial cell cycle.
Figures
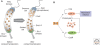

Similar articles
-
Connecting the dots of the bacterial cell cycle: Coordinating chromosome replication and segregation with cell division.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 May;53:2-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.11.012. Epub 2015 Dec 17. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26706151 Review.
-
Novel Divisome-Associated Protein Spatially Coupling the Z-Ring with the Chromosomal Replication Terminus in Caulobacter crescentus.mBio. 2020 Apr 28;11(2):e00487-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00487-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32345642 Free PMC article.
-
Guiding divisome assembly and controlling its activity.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015 Apr;24:60-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25636132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The great divide: coordinating cell cycle events during bacterial growth and division.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008 Apr;11(2):94-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Apr 7. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18396093 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Division site selection in rod-shaped bacteria.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009 Dec;12(6):683-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2009.10.002. Epub 2009 Nov 1. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19884039 Review.
Cited by
-
Artificial modulation of cell width significantly affects the division time of Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 20;10(1):17847. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74778-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33082450 Free PMC article.
-
Choreography of the Mycobacterium replication machinery during the cell cycle.mBio. 2015 Feb 17;6(1):e02125-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02125-14. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25691599 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-associated DNA transport machines.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Jul;2(7):a000406. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000406. Epub 2010 Jun 23. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20573715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patatin-like phospholipase CapV in Escherichia coli - morphological and physiological effects of one amino acid substitution.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2022 May 11;8(1):39. doi: 10.1038/s41522-022-00294-z. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2022. PMID: 35546554 Free PMC article.
-
Transient enhanced cell division by blocking DNA synthesis in Escherichia coli.Microbiology (Reading). 2020 Jun;166(6):516-521. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000888. Microbiology (Reading). 2020. PMID: 32118529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams DE, Shekhtman EM, Zechiedrich EL, Schmid MB, Cozzarelli NR 1992. The role of topoisomerase IV in partitioning bacterial replicons and the structure of catenated intermediates in DNA replication. Cell 71:277–288 - PubMed
-
- Aussel L, Barre FX, Aroyo M, Stasiak A, Stasiak AZ, Sherratt D 2002. FtsK is a DNA motor protein that activates chromosome dimer resolution by switching the catalytic state of the XerC and XerD recombinases. Cell 108:195–205 - PubMed
-
- Bastedo DP, Marczynski GT 2009. CtrA response regulator binding to the Caulobacter chromosome replication origin is required during nutrient and antibiotic stress as well as during cell cycle progression. Mol Microbiol 72:139–154 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
