The regulation of the p53-mediated stress response by MDM2 and MDM4
- PMID: 20182601
- PMCID: PMC2827903
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000968
The regulation of the p53-mediated stress response by MDM2 and MDM4
Abstract
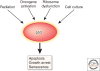
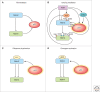
Exquisite control of the activity of p53 is necessary for mammalian survival. Too much p53 is lethal, whereas too little permits tumorigenesis. MDM2 and MDM4 are structurally related proteins critical for the control of p53 activity during development, homeostasis, and the response to stress. These two essential proteins regulate both the activation of p53 in response to stress and the recovery of cells following resolution of the damage, yet both are oncogenic when overexpressed. Thus, multiple regulatory circuits ensure that their activities are fine-tuned to promote tumor-free survival. Numerous diverse stressors activate p53, and much research has gone into trying to find commonalities between them that would explain the mechanism by which p53 becomes active. It is now clear that although these diverse stressors activate p53 by different biochemical pathways, one common feature is the effort they direct, through a variety of means, toward disrupting the functions of both MDM2 and MDM4. This article provides an overview of the relationship between MDM2 and MDM4, features the various biochemical mechanisms by which p53 is activated through inhibition of their functions, and proposes some emerging areas for investigation of the p53-mediated stress response.
Figures
References
-
- Bond GL, Hu W, Bond EE, Robins H, Lutzker SG, Arva NC, Bargonetti J, Bartel F, Taubert H, Wuerl P, et al. 2004. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 promoter attenuates the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in humans. Cell 119:591–602 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
