Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infraction after High Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin Infusion
- PMID: 20182639
- PMCID: PMC2825772
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/861370
Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infraction after High Dose Intravenous Immunoglobulin Infusion
Abstract
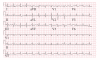
Intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIgs) are used for several indications, including autoimmune conditions. IVIg treatment is associated with several possible adverse reactions including induction of a hypercoagulable state. We report a 76-year-old woman treated with IVIg for myasthenia gravis, which developed chest pain and weakness following IVIg infusion. The symptoms were associated with ST segment depression in V4-6 and elevated troponin levels. The patient was diagnosed with non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). The patient had no significant risk factor besides age and a cardiac perfusion scan was interpreted as normal (the patient refused to undergo cardiac catheterization). This case is compatible with IVIg-induced hypercoagulability resulting in NSTEMI. Cardiac evaluation should therefore be considered prior to initiation of IVIg treatment especially in patients with multiple cardiovascular risks.
References
-
- Vani J, Elluru S, Negi VS, et al. Role of natural antibodies in immune homeostasis: IVIg perspective. Autoimmunity Reviews. 2008;7(6):440–444. - PubMed
-
- Dalakas MC. Intravenous immunoglobulin in autoimmune neuromuscular diseases. Journal of the American Medical Association. 2004;291(19):2367–2375. - PubMed
-
- Gold R, Stangel M, Dalakas MC. Drug insight: the use of intravenous immunoglobulin in neurology—therapeutic considerations and practical issues. Nature Clinical Practice Neurology. 2007;3(1):36–44. - PubMed
-
- Bayry J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Kazatchkine MD, Kaveri SV. Monoclonal antibody and intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for rheumatic diseases: rationale and mechanisms of action. Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology. 2007;3(5):262–272. - PubMed
-
- Kamali S, Cefle A, Sayarlioglu M, et al. Experience with monthly, high-dose, intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in patients with different connective tissue diseases. Rheumatology International. 2005;25(3):211–214. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources