Larval excretory-secretory products from the parasite Schistosoma mansoni modulate HSP70 protein expression in defence cells of its snail host, Biomphalaria glabrata
- PMID: 20182834
- PMCID: PMC3006636
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-010-0176-z
Larval excretory-secretory products from the parasite Schistosoma mansoni modulate HSP70 protein expression in defence cells of its snail host, Biomphalaria glabrata
Abstract
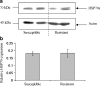
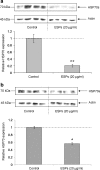
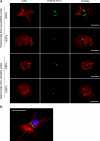
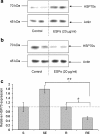
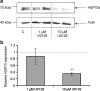
Synthesis of heat shock proteins (HSPs) following cellular stress is a response shared by many organisms. Amongst the HSP family, the approximately 70 kDa HSPs are the most evolutionarily conserved with intracellular chaperone and extracellular immunoregulatory functions. This study focused on the effects of larval excretory-secretory products (ESPs) from the parasite Schistosoma mansoni on HSP70 protein expression levels in haemocytes (defence cells) from its snail intermediate host Biomphalaria glabrata. S. mansoni larval stage ESPs are known to interfere with haemocyte physiology and behaviour. Haemocytes from two different B. glabrata strains, one which is susceptible to S. mansoni infection and one which is resistant, both showed reduced HSP70 protein levels following 1 h challenge with S. mansoni ESPs when compared to unchallenged controls; however, the reduction observed in the resistant strain was less marked. The decline in intracellular HSP70 protein persisted for at least 5 h in resistant snail haemocytes only. Furthermore, in schistosome-susceptible snails infected by S. mansoni for 35 days, haemocytes possessed approximately 70% less HSP70. The proteasome inhibitor, MG132, partially restored HSP70 protein levels in ESP-challenged haemocytes, demonstrating that the decrease in HSP70 was in part due to intracellular degradation. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signalling pathway appears to regulate HSP70 protein expression in these cells, as the mitogen-activated protein-ERK kinase 1/2 (MEK1/2) inhibitor, U0126, significantly reduced HSP70 protein levels. Disruption of intracellular HSP70 protein expression in B. glabrata haemocytes by S. mansoni ESPs may be a strategy employed by the parasite to manipulate the immune response of the intermediate snail host.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Disruption of ERK signalling in Biomphalaria glabrata defence cells by Schistosoma mansoni: implications for parasite survival in the snail host.Dev Comp Immunol. 2008;32(12):1561-71. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.05.014. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Dev Comp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18619674
-
Nitric oxide production by Biomphalaria glabrata haemocytes: effects of Schistosoma mansoni ESPs and regulation through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway.Parasit Vectors. 2009 Apr 22;2(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-2-18. Parasit Vectors. 2009. PMID: 19386102 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the gene expression profiles of haemocytes from schistosome-susceptible and -resistant biomphalaria glabrata exposed to Schistosoma mansoni excretory-secretory products.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 24;9(3):e93215. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093215. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24663063 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic modulation, stress and plasticity in susceptibility of the snail host, Biomphalaria glabrata, to Schistosoma mansoni infection.Int J Parasitol. 2016 Jun;46(7):389-94. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Int J Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27056272 Review.
-
Are Biomphalaria snails resistant to Schistosoma mansoni?J Helminthol. 2005 Sep;79(3):187-91. doi: 10.1079/joh2005299. J Helminthol. 2005. PMID: 16153311 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-Seq reveals infection-induced gene expression changes in the snail intermediate host of the carcinogenic liver fluke, Opisthorchis viverrini.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Mar 27;8(3):e2765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002765. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 24676090 Free PMC article.
-
A genome sequence for Biomphalaria pfeifferi, the major vector snail for the human-infecting parasite Schistosoma mansoni.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023 Mar 24;17(3):e0011208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011208. eCollection 2023 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2023. PMID: 36961841 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Biomphalaria glabrata hemocyte subpopulations possess shared schistosome glycans and receptors capable of binding larval glycoconjugates.Exp Parasitol. 2013 Jan;133(1):28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Exp Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23085445 Free PMC article.
-
Reversing the resistance phenotype of the Biomphalaria glabrata snail host Schistosoma mansoni infection by temperature modulation.PLoS Pathog. 2012;8(4):e1002677. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002677. Epub 2012 Apr 26. PLoS Pathog. 2012. PMID: 22577362 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Schistosoma japonicum excretory/secretory proteins and their interactions with host immune system.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023786. Epub 2011 Aug 24. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21887319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buckley BA, Owen ME, Hofmann GE. Adjusting the thermostat: The threshold induction temperature for the heat shock response in intertidal mussels (genus Mytilus) changes as a function of thermal history. J Exp Biol. 2001;204:3571–3579. - PubMed
-
- Clayton ME, Steinmann R, Fent K. Different expression patterns of heat shock proteins hsp 60 and hsp 70 in zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) exposed to copper and tributyltin. Aquat Toxicol. 2000;47:213–226. doi: 10.1016/S0166-445X(99)00022-3. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

