Synthesis of guanosine and deoxyguanosine phosphoramidites with cross-linkable thioalkyl tethers for direct incorporation into RNA and DNA
- PMID: 20183575
- PMCID: PMC2829721
- DOI: 10.1080/15257770903368385
Synthesis of guanosine and deoxyguanosine phosphoramidites with cross-linkable thioalkyl tethers for direct incorporation into RNA and DNA
Abstract
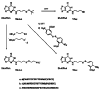
We describe the synthesis of protected phosphoramidites of deoxyriboguanosine and guanosine derivatives containing a thiopropyl tether at the guanine N2 (7a,b) for site-specific crosslinking from the minor groove of either DNA or RNA to a thiol of a protein or another nucleic acid. The thiol is initially protected as a tert-butyl disulfide that is stable during oligonucleotide synthesis. While the completed oligonucleotide is still attached to the support, or after purification, the tert-butyl thiol can readily be removed or replaced by thioethylamine or 5-thio-2-nitrobenzoic acid, which have more favorable crosslinking rates.
References
-
- Verdine GL, Norman DPG. Covalent trapping of protein-DNA complexes. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 2003;72:337–366. - PubMed
-
- Glick GD. Design, synthesis, and analysis of conformationally constrained nucleic acids. Biopolymers (Nucleic Acid Sciences) 1998;48:83–96. - PubMed
-
- Huang H, Chopra R, Verdine GL, Harrison SC. Structure of a covalently trapped catalytic complex of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: implications for drug resistance. Science. 1998;282:1669–1675. - PubMed
-
- He C, Verdine GL. Trapping distinct structural states of a protein/DNA interaction through disulfide crosslinking. Chemistry & Biology. 2002;9:1297–1303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources