Thiophosphate analogs of c-di-GMP: impact on polymorphism
- PMID: 20183589
- PMCID: PMC2829739
- DOI: 10.1080/15257770903044523
Thiophosphate analogs of c-di-GMP: impact on polymorphism
Abstract
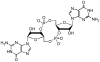
Seven phosphorothioate analogs of c-di-GMP (all diastereomers of mono-, di-, and trithiophosphates) were prepared to assess the impact of the thioate substitutions on c-di-GMP polymorphism using 1D (1)H and (31)P NMR, along with 2D NOESY and DOSY, for both the Na(+) and K(+) salts. The K(+) salts display more extensive higher order complex formation than the Na(+) salts, resulting primarily in octamolecular complexes with K(+), but tetramolecular complexes with Na(+). Further, the presence of one or two [S(P)] sulfurs specifically stabilizes anti complexes and/or destabilizes syn complexes, while the presence of two [S(P)] sulfurs promotes extensive aggregation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
One-flask syntheses of c-di-GMP and the [Rp,Rp] and [Rp,Sp] thiophosphate analogues.Org Lett. 2010 Jul 16;12(14):3269-71. doi: 10.1021/ol101236b. Org Lett. 2010. PMID: 20572672 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and characterization of C8 analogs of c-di-GMP.Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2011 Nov;30(11):961-78. doi: 10.1080/15257770.2011.624567. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2011. PMID: 22060558
-
Polymorphism of the signaling molecule c-di-GMP.J Am Chem Soc. 2006 May 31;128(21):7015-24. doi: 10.1021/ja0613714. J Am Chem Soc. 2006. PMID: 16719482 Free PMC article.
-
The bacterial second messenger c-di-GMP: probing interactions with protein and RNA binding partners using cyclic dinucleotide analogs.Org Biomol Chem. 2012 Dec 14;10(46):9113-29. doi: 10.1039/c2ob26724a. Epub 2012 Oct 29. Org Biomol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23108253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3',5'-Cyclic diguanylic acid: a small nucleotide that makes big impacts.Chem Soc Rev. 2010 Aug;39(8):2914-24. doi: 10.1039/b914942m. Epub 2010 Jun 25. Chem Soc Rev. 2010. PMID: 20577685 Review.
Cited by
-
10th anniversary of discovering cGAMP: synthesis and beyond.Org Chem Front. 2023 Feb 21;10(4):1086-1098. doi: 10.1039/d2qo02033e. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Org Chem Front. 2023. PMID: 37144138 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking P(V): Reagents for chiral phosphorothioate synthesis.Science. 2018 Sep 21;361(6408):1234-1238. doi: 10.1126/science.aau3369. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Science. 2018. PMID: 30072577 Free PMC article.
-
One-flask syntheses of c-di-GMP and the [Rp,Rp] and [Rp,Sp] thiophosphate analogues.Org Lett. 2010 Jul 16;12(14):3269-71. doi: 10.1021/ol101236b. Org Lett. 2010. PMID: 20572672 Free PMC article.
-
Bifacial nucleoside as a surrogate for both T and A in duplex DNA.J Am Chem Soc. 2011 May 11;133(18):6926-9. doi: 10.1021/ja201397e. Epub 2011 Apr 15. J Am Chem Soc. 2011. PMID: 21495708 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of c-di-GMP derivatives resistant to an EAL domain phosphodiesterase.Biochemistry. 2013 Jan 15;52(2):365-77. doi: 10.1021/bi301510v. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23256840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romling U, Amikam D. Cyclic di-GMP as a second messenger. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2006;9:218–228. - PubMed
-
- Jenal U, Malone J. Mechanisms of cyclic-di-GMP signaling in bacteria. Annual Review of Genetics. 2006;40:385–407. - PubMed
-
- Cotter PA, Stibitz S. c-di-GMP-mediated regulation of virulence and biofilm formation. Current Opinion in Microbiology. 2007;10:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Karaolis DKR, Means TK, Yang D, Takahashi M, Yoshimura T, Muraille E, Philpott D, Schroeder JT, Hyodo M, Hayakawa Y, Talbot BG, Brouillette E, Malouin F. Bacterial c-di-GMP is an immunostimulatory molecule. Journal of Immunology. 2007;178:2171–2181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
