Carbocyclic thymidine analogues for use as potential therapeutic agents
- PMID: 20183606
- PMCID: PMC3701155
- DOI: 10.1080/15257770903091920
Carbocyclic thymidine analogues for use as potential therapeutic agents
Abstract
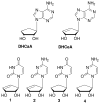
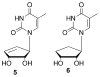
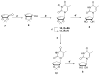
The discovery of azidothymidine's (AZT) activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) provided strong rationale for the design of additional thymidine analogues. One drawback of many nucleoside analogues is the toxicity that often arises due to phosphorylation by cellular kinases. In order to overcome this problem, a number of truncated nucleosides lacking the 4'-hydroxymethyl group have been synthesized. In that regard, the synthesis and preliminary biological results for two truncated carbocyclic thymidine analogues are presented herein.
Figures

References
-
- De Clercq E. New approaches toward anti-HIV chemotherapy. J Med Chem. 2005;48:1297–1313. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq E. Antiviral activity spectrum and target of action of different classes of Nucleoside analogues. Nucleosides Nucleotides. 1994;13:1271–1295.
-
- Robins RK, Revankar GR. Advances in Anti Viral Drug Design. JAI Press; Greenwich: 1993.
-
- Griengl H, Hayden W, Penn G, De Clercq E, Rosenwirth B. Phosphonoformate and phospho-noacetate derivatives of 5-substituted 2′-deoxyuridines: synthesis and antiviral activity. J Med Chem. 1988;31:1831–1839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
