Functions of ICC-like cells in the urinary tract and male genital organs
- PMID: 20184664
- PMCID: PMC3828839
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01043.x
Functions of ICC-like cells in the urinary tract and male genital organs
Abstract
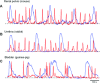
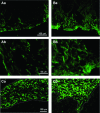
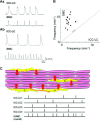
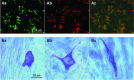
Interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC)-like cells (ICC-LCs) have been identified in many regions of the urinary tract and male genital organs by immunohistochemical studies and electron microscopy. ICC-LCs are characterized by their spontaneous electrical and Ca(2+) signalling and the cellular mechanisms of their generation have been extensively investigated. Spontaneous activity in ICC-LCs rises from the release of internally stored Ca(2+) and the opening of Ca(2+)-activated Cl(-) channels to generate spontaneous transient depolarizations (STDs) in a manner not fundamentally dependent on Ca(2+) influx through L-type voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channels. Since urogenital ICC-LCs have been identified by their immunoreactivity to Kit (CD117) antibodies, the often-used specific marker for ICC in the gastrointestinal tract, their functions have been thought likely to be similar. Thus ICC-LCs in the urogenital tract might be expected to act as either electrical pacemaker cells to drive the smooth muscle wall or as intermediaries in neuromuscular transmission. However, present knowledge of the functions of ICC-LCs suggests that their functions are not so predetermined, that their functions may be very region specific, particularly under pathological conditions. In this review, we summarize recent advances in our understanding of the location and function of ICC-LCs in various organs of the urogenital system. We also discuss several unsolved issues regarding the identification, properties and functions of ICC-LCs in various urogenital regions in health and disease.
Figures
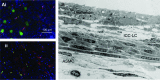
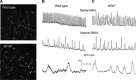
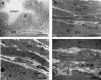
References
-
- Sanders KM, Koh SD, Ward SM. Interstitial cells of Cajal as pacemakers in the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:307–43. - PubMed
-
- Brading AF, McCloskey KD. Mechanisms of disease: specialized interstitial cells of the urinary tract–an assessment of current knowledge. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005;2:546–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

