DNA linking number change induced by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins
- PMID: 20185570
- PMCID: PMC2887952
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkq078
DNA linking number change induced by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins
Abstract
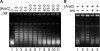
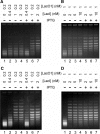
Sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins play a key role in many fundamental biological processes, such as transcription, DNA replication and recombination. Very often, these DNA-binding proteins introduce structural changes to the target DNA-binding sites including DNA bending, twisting or untwisting and wrapping, which in many cases induce a linking number change (Delta Lk) to the DNA-binding site. Due to the lack of a feasible approach, Delta Lk induced by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins has not been fully explored. In this paper we successfully constructed a series of DNA plasmids that carry many tandem copies of a DNA-binding site for one sequence-specific DNA-binding protein, such as lambda O, LacI, GalR, CRP and AraC. In this case, the protein-induced Delta Lk was greatly amplified and can be measured experimentally. Indeed, not only were we able to simultaneously determine the protein-induced Delta Lk and the DNA-binding constant for lambda O and GalR, but also we demonstrated that the protein-induced Delta Lk is an intrinsic property for these sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. Our results also showed that protein-mediated DNA looping by AraC and LacI can induce a Delta Lk to the plasmid DNA templates. Furthermore, we demonstrated that the protein-induced Delta Lk does not correlate with the protein-induced DNA bending by the DNA-binding proteins.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Protein-induced DNA linking number change by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins and its biological effects.Biophys Rev. 2016 Nov;8(Suppl 1):123-133. doi: 10.1007/s12551-016-0239-1. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Biophys Rev. 2016. PMID: 28510217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-induced DNA linking number change by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins and its biological effects.Biophys Rev. 2016 Sep;8(3):197-207. doi: 10.1007/s12551-016-0204-z. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Biophys Rev. 2016. PMID: 28510223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cooperative and anticooperative effects in binding of the first and second plasmid Osym operators to a LacI tetramer: evidence for contributions of non-operator DNA binding by wrapping and looping.J Mol Biol. 1996 Aug 2;260(5):697-717. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0431. J Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8709149
-
Thermodynamics of the interactions of lac repressor with variants of the symmetric lac operator: effects of converting a consensus site to a non-specific site.J Mol Biol. 1997 Apr 18;267(5):1186-206. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.0920. J Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9150406
-
Interactions between DNA-bound transcriptional regulators of the Escherichia coli gal operon.Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 4;31(30):6980-9. doi: 10.1021/bi00145a016. Biochemistry. 1992. PMID: 1637832
Cited by
-
Protein-induced DNA linking number change by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins and its biological effects.Biophys Rev. 2016 Nov;8(Suppl 1):123-133. doi: 10.1007/s12551-016-0239-1. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Biophys Rev. 2016. PMID: 28510217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial transcription during growth arrest.Transcription. 2021 Aug;12(4):232-249. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2021.1968761. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Transcription. 2021. PMID: 34486930 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA supercoiling, a critical signal regulating the basal expression of the lac operon in Escherichia coli.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 14;6:19243. doi: 10.1038/srep19243. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26763930 Free PMC article.
-
Methods to Quantitatively Measure Topological Changes Induced by DNA-Binding Proteins In Vivo and In Vitro.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2819:421-441. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3930-6_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39028517 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosomal organization of transcription: in a nutshell.Curr Genet. 2018 Jun;64(3):555-565. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0785-5. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 29184972 Review.
References
-
- Kaguni JM. DnaA: controlling the initiation of bacterial DNA replication and more. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2006;60:351–375. - PubMed
-
- Mott ML, Berger JM. DNA replication initiation: mechanisms and regulation in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007;5:343–354. - PubMed
-
- Alfano C, McMacken R. Ordered assembly of nucleoprotein structures at the bacteriophage lambda replication origin during the initiation of DNA replication. J. Biol. Chem. 1989;264:10699–10708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

