A randomized controlled study comparing once-weekly to every-2-week and every-4-week dosing of epoetin alfa in CKD patients with anemia
- PMID: 20185602
- PMCID: PMC2849701
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.06770909
A randomized controlled study comparing once-weekly to every-2-week and every-4-week dosing of epoetin alfa in CKD patients with anemia
Abstract
Background and objectives: Extended-interval dosing of epoetin alfa (EPO) is commonly used to treat anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). This study aimed to demonstrate that EPO dosed every 2 weeks (Q2W) and every 4 weeks (Q4W) was noninferior to once-weekly (QW) dosing.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: 430 anemic subjects with stage 3 to 4 CKD receiving a stable QW dose of EPO were randomized 1:1:2 to QW, Q2W, and Q4W dosing for 36 weeks. Hemoglobin (Hb) was measured weekly, and the dose of EPO was adjusted to maintain an Hb level of 11.0 to 11.9 g/dl. The primary endpoint was change in Hb from baseline to the average of the last 12 weeks of treatment.
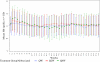
Results: Both the Q2W and Q4W dosing groups were noninferior to the QW group. The estimated difference of the mean change in Hb between Q2W and QW was -0.03 g/dl; and between Q4W and QW was -0.09 g/dl. From weeks 13 to 37, the mean percentage of weeks per subject with Hb 10.0 to 11.9 g/dl, inclusive, was 81% for QW, 81% for Q2W, and 75% for Q4W. Death occurred, respectively, in 4%, 3%, and 4%; thromboembolic vascular events occurred in 3%, 5%, and 3%; and serious adverse events occurred in 22%, 26%, and 26% of subjects.
Conclusions: Q2W and Q4W EPO dosing maintained Hb levels in subjects with stage 3 to 4 CKD. Deaths, thromboembolic vascular events, and serious adverse events were comparable across the dosing groups.
Figures
References
-
- Drawz P, Rahman M: In the clinic Chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med 150: ITC2-1–15: quiz ITC12-16, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Astor BC, Muntner P, Levin A, Eustace JA, Coresh J: Association of kidney function with anemia: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1988–1994). Arch Intern Med 162: 1401–1408, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Holland DC, Lam M: Predictors of hospitalization and death among pre-dialysis patients: A retrospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15: 650–658, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Levin A, Djurdjev O, Duncan J, Rosenbaum D, Werb R: Haemoglobin at time of referral prior to dialysis predicts survival: An association of haemoglobin with long-term outcomes. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21: 370–377, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Klang B, Bjorvell H, Clyne N: Quality of life in predialytic uremic patients. Qual Life Res 5: 109–116, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

