Oral tolvaptan is safe and effective in chronic hyponatremia
- PMID: 20185637
- PMCID: PMC2844305
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2009080857
Oral tolvaptan is safe and effective in chronic hyponatremia
Erratum in
- J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Aug;21(8):1407
Abstract
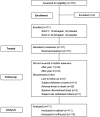
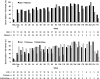
Vasopressin antagonists increase the serum sodium concentration in patients who have euvolemia and hypervolemia with hyponatremia in the short term (</=30 days), but their safety and efficacy with longer term administration is unknown. SALTWATER was a multicenter, open-label extension of the Study of Ascending Levels of Tolvaptan in Hyponatremia (SALT-1 and SALT-2). In total, 111 patients with hyponatremia received oral tolvaptan for a mean follow-up of 701 days, providing 77,369 patient-days of exposure. All patients had hyponatremia at randomization in SALT-1 and SALT-2, and 85% continued to have hyponatremia at entry in SALTWATER. The most common adverse effects attributed to tolvaptan were pollakiuria, thirst, fatigue, dry mouth, polydipsia, and polyuria. Six drug-related adverse effects led to study discontinuation. The increase in serum sodium exceeded the desired 1 mmol/L per h at initiation in five patients. Hypernatremia (>145 mmol/L) led to discontinuation in one patient. Mean serum sodium increased from 130.8 mmol/L at baseline to >135 mmol/L throughout the observation period (P < 0.001 versus baseline at most points). Responses were comparable between patients with euvolemia and those with heart failure but more modest in patients with cirrhosis. In conclusion, prolonged administration of tolvaptan maintains an increased serum sodium with an acceptable margin of safety.
Figures
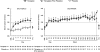
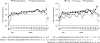
Comment in
-
Treatment of chronic hyponatremia: now we know how, but do we know when or if?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010 Apr;21(4):552-5. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010020157. Epub 2010 Feb 25. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20185636 No abstract available.
-
Hyponatremia: Prolonged use of the vasopressin antagonist tolvaptan is a safe and effective treatment for hyponatremia.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010 Jun;6(6):315. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2010.61. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20508668 No abstract available.
References
-
- Greenberg A, Verbalis JG: Vasopressin receptor antagonists. Kidney Int 69: 2124– 2130, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Annane D, Decaux G, Smith N: Efficacy and safety of oral conivaptan, a vasopressin-receptor antagonist, evaluated in a randomized, controlled trial in patients with euvolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia. Am J Med Sci 337: 28– 36, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Decaux G: Long-term treatment of patients with inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone by the vasopressin receptor antagonist conivaptan, urea, or furosemide. Am J Med 110: 582– 584, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Ghali JK, Koren MJ, Taylor JR, Brooks-Asplund E, Fan K, Long WA, Smith N: Efficacy and safety of oral conivaptan: A V1A/V2 vasopressin receptor antagonist, assessed in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial in patients with euvolemic or hypervolemic hyponatremia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91: 2145– 2152, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Gines P, Wong F, Watson H, Milutinovic S, del Arbol LR, Olteanu D: Effects of satavaptan, a selective vasopressin V(2) receptor antagonist, on ascites and serum sodium in cirrhosis with hyponatremia: A randomized trial. Hepatology 48: 204– 213, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

