Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), a cofactor for nNOS, restores gastric emptying and nNOS expression in female diabetic rats
- PMID: 20185690
- PMCID: PMC2867432
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00450.2009
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), a cofactor for nNOS, restores gastric emptying and nNOS expression in female diabetic rats
Abstract
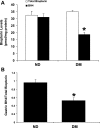
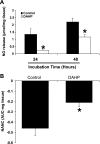
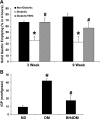
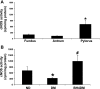
Gastroparesis is a debilitating disease predominantly affecting young women. Recently, dysregulation of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in myenteric plexus neurons has been implicated for delayed solid gastric emptying/gastroparesis in diabetic patients. In this study, we have explored the role of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), a major cofactor for nNOS activity and NO synthesis in diabetic gastroparesis. Diabetes was induced with single injection of streptozotocin (55 mg/kg body wt, ip) in female rats, with experiments performed on week 3 or 9 following induction, with or without 3-wk BH4 supplementation. Gastric pyloric BH4 levels were significantly decreased in diabetic female rats compared with control (18.6 +/- 1.45 vs. 31.0 +/- 2.31 pmol/mg protein). In vitro studies showed that 2,4-diamino-6-hydroxypyrimidine (DAHP), an inhibitor of BH4 synthesis, significantly decreased gastric NO release and nitrergic relaxation. Three-week dietary supplementation of BH4 either from day 1 or week 6 significantly attenuated diabetes-induced delayed gastric emptying for solids (3 wk: BH4, 67 +/- 6.7 vs. diabetic, 36.05 +/- 7.09; 9 wk: BH4, 57 +/- 8.45 vs. diabetic, 33 +/- 9.91) and diabetes-induced reduction in pyloric nNOS-alpha protein expression in female rats. Supplementation of BH4 significantly restored gastric nNOS-alpha dimerization in 9-wk-old diabetic female rats. In addition, BH4 treatment reversed (17.23 +/- 5.81 vs. 42.0 +/- 2.70 mmHg x s) the diabetes-induced changes in intragastric pressures (IGP) and gastric pyloric nitrergic relaxation (-0.62 +/- 0.01 vs. -0.22 +/- 0.07). BH4 deficiency plays a critical role in diabetes-induced alterations including delayed solid gastric emptying, increased IGP, reduced pyloric nitrergic relaxation, and nNOS-alpha expression in female rats. Supplementation of BH4 accelerates gastric emptying by restoring nitrergic system in diabetic female rats. Therefore, BH4 supplementation is a potential therapeutic option for female patients of diabetic gastroparesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sepiapterin reverses the changes in gastric nNOS dimerization and function in diabetic gastroparesis.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010 Dec;22(12):1325-31, e351-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2010.01588.x. Epub 2010 Aug 22. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010. PMID: 20731778 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes induces sex-dependent changes in neuronal nitric oxide synthase dimerization and function in the rat gastric antrum.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Mar;292(3):G725-33. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00406.2006. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17347455 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic estrogen deficiency causes gastroparesis by altering neuronal nitric oxide synthase function.Dig Dis Sci. 2013 Jun;58(6):1507-15. doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2610-4. Epub 2013 Mar 17. Dig Dis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23504347 Free PMC article.
-
Gender bias in gastroparesis: is nitric oxide the answer?Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Sep;56(9):2520-7. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1735-6. Epub 2011 May 11. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21559738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiological significance of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the gastrointestinal tract.J Gastroenterol. 2003;38(5):421-30. doi: 10.1007/s00535-003-1094-y. J Gastroenterol. 2003. PMID: 12768383 Review.
Cited by
-
Supplementation of 17β-Estradiol Normalizes Rapid Gastric Emptying by Restoring Impaired Nrf2 and nNOS Function in Obesity-Induced Diabetic Ovariectomized Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jul 3;9(7):582. doi: 10.3390/antiox9070582. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32635208 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of GSK-3β restores delayed gastric emptying in obesity-induced diabetic female mice.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020 Oct 1;319(4):G481-G493. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00227.2020. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32812777 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroparesis: a turning point in understanding and treatment.Gut. 2019 Dec;68(12):2238-2250. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318712. Epub 2019 Sep 28. Gut. 2019. PMID: 31563877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sepiapterin reverses the changes in gastric nNOS dimerization and function in diabetic gastroparesis.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010 Dec;22(12):1325-31, e351-2. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2010.01588.x. Epub 2010 Aug 22. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2010. PMID: 20731778 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular handoffs in nitrergic neurotransmission.Front Med (Lausanne). 2014 Apr 10;1:8. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2014.00008. eCollection 2014. Front Med (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25705621 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andrew PJ, Mayer B. Enzymatic function of nitric oxide synthases. Cardiovasc Res 43: 521–531, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Bai Y, Xu MJ, Yang X, Xu C, Gao J, Zou DW, Li ZS. A systemic review on intrapyloric botulinum toxin injection for gastroparesis. Digestion 81: 27–34, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Bush PA, Gonzalez NE, Ignarro LJ. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide and citrulline from L- arginine by constitutive nitric oxide synthase present in rabbit corpus cavernosum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186: 308–314, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Cai S, Alp NJ, McDonald D, Smith I, Kay J, Canevari L, Heales S, Channon KM. GTP cyclohydrolase I gene transfer augments intracellular tetrahydrobiopterin in human endothelial cells: effects on nitric oxide synthase activity, protein levels and dimerisation. Cardiovasc Res 55: 838–849, 2002 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

