Accelerated increase in serum interleukin-1 receptor antagonist starts 6 years before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: Whitehall II prospective cohort study
- PMID: 20185814
- PMCID: PMC2857902
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-1199
Accelerated increase in serum interleukin-1 receptor antagonist starts 6 years before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: Whitehall II prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Although interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) treatment is associated with improved beta-cell function and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes, its role in the development of type 2 diabetes remains unclear. We used repeated measurements to characterize IL-1Ra trajectories in individuals who developed type 2 diabetes.
Research design and methods: This case-cohort study, nested within the Whitehall II cohort, was based on 335 incident type 2 diabetes cases and 2,475 noncases. We measured serum IL-1Ra levels at up to three time points per individual and estimated retrospective trajectories of IL-1Ra before diabetes diagnosis (case subjects) or end of follow-up (control subjects) using multilevel analysis. Models were adjusted for age, sex, and ethnicity.
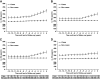
Results: IL-1Ra levels were already higher in the case than control subjects 13 years before diabetes diagnosis/end of follow-up (mean [95% CI] 302 [290-314] vs. 244 [238-249] pg/ml). In control subjects, IL-1Ra levels showed a modest linear increase throughout the study period. In case subjects, IL-1Ra trajectories were parallel to those in control subjects until 6 years (95% CI 7.5-4.5) before diagnosis and then rose steeply to 399 (379-420) pg/ml at the time of diagnosis (P < 0.0001 for slope difference). Adjustment for BMI and waist circumference as time-varying covariates had little impact on these trajectories.
Conclusions: We show elevated IL-1Ra levels for 13 years and an accelerated increase during the last 6 years before type 2 diabetes diagnosis, indicating the presence of an anti-inflammatory response that may act to counterbalance the metabolic and immunologic disturbances that precede type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Elevated levels of the anti-inflammatory interleukin-1 receptor antagonist precede the onset of type 2 diabetes: the Whitehall II study.Diabetes Care. 2009 Mar;32(3):421-3. doi: 10.2337/dc08-1161. Epub 2008 Dec 10. Diabetes Care. 2009. PMID: 19073760 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin, biomarkers of inflammation and changes in cardiac autonomic function: Whitehall II study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017 Dec 1;16(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12933-017-0634-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2017. PMID: 29195493 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin trajectories before type 2 diabetes diagnosis: Whitehall II study.Diabetes Care. 2012 Dec;35(12):2540-7. doi: 10.2337/dc11-2263. Epub 2012 Aug 28. Diabetes Care. 2012. PMID: 22933430 Free PMC article.
-
Gender-based dimorphic pattern for interleukin-1 receptor antagonist in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabetes Metab. 2008 Feb;34(1):75-81. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2007.10.006. Epub 2008 Feb 1. Diabetes Metab. 2008. PMID: 18243027
-
Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) and IL-1Ra producing mesenchymal stem cells as modulators of diabetogenesis.Autoimmunity. 2010 Jun;43(4):255-63. doi: 10.3109/08916930903305641. Autoimmunity. 2010. PMID: 19845478 Review.
Cited by
-
Double-blind, randomized study evaluating the glycemic and anti-inflammatory effects of subcutaneous LY2189102, a neutralizing IL-1β antibody, in patients with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2013 Aug;36(8):2239-46. doi: 10.2337/dc12-1835. Epub 2013 Mar 20. Diabetes Care. 2013. PMID: 23514733 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of different sources of fish and camelina sativa oil on immune cell and adipose tissue mRNA expression in subjects with abnormal fasting glucose metabolism: a randomized controlled trial.Nutr Diabetes. 2019 Jan 9;9(1):1. doi: 10.1038/s41387-018-0069-2. Nutr Diabetes. 2019. PMID: 30683848 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inflammation in the Pathophysiology and Therapy of Cardiometabolic Disease.Endocr Rev. 2019 Aug 1;40(4):1080-1091. doi: 10.1210/er.2019-00002. Endocr Rev. 2019. PMID: 31127805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are current diagnostic guidelines delaying early detection of dysglycemic states? Time for new approaches.Endocrine. 2013 Aug;44(1):66-9. doi: 10.1007/s12020-013-9873-6. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Endocrine. 2013. PMID: 23325362
-
Differences in insulin sensitivity, lipid metabolism and inflammation between young adult Pakistani and Norwegian patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross sectional study.BMC Endocr Disord. 2013 Oct 22;13:49. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-13-49. BMC Endocr Disord. 2013. PMID: 24148878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, Butler PC. β-cell deficient and increased β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003;52:102–110 - PubMed
-
- Kolb H, Mandrup-Poulsen T. An immune origin of type 2 diabetes? Diabetologia 2005;48:1038–1050 - PubMed
-
- Herder C, Baumert J, Thorand B, Koenig W, de Jager W, Meisinger C, Illig T, Martin S, Kolb H. Chemokines as risk factors for type 2 diabetes: results from the MONICA/KORA Augsburg study, 1984–2002. Diabetologia 2006;49:921–929 - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006;444:860–867 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL036310/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G19/35/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0100222/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HS-06516/HS/AHRQ HHS/United States
- R37 AG013196/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013196/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RG/07/008/23674/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G8802774/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0902037/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0501184/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- AG-13196/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

