Unique arrangement of alpha- and beta-cells in human islets of Langerhans
- PMID: 20185817
- PMCID: PMC2857900
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-1177
Unique arrangement of alpha- and beta-cells in human islets of Langerhans
Abstract
Objective: It is generally admitted that the endocrine cell organization in human islets is different from that of rodent islets. However, a clear description of human islet architecture has not yet been reported. The aim of this work was to describe our observations on the arrangement of human islet cells.
Research design and methods: Human pancreas specimens and isolated islets were processed for histology. Sections were analyzed by fluorescence microscopy after immunostaining for islet hormones and endothelial cells.
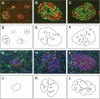
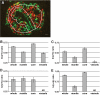
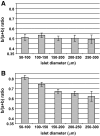
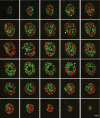
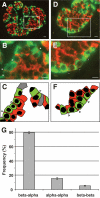
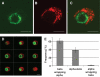
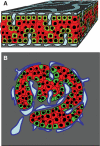
Results: In small human islets (40-60 mum in diameter), beta-cells had a core position, alpha-cells had a mantle position, and vessels laid at their periphery. In bigger islets, alpha-cells had a similar mantle position but were found also along vessels that penetrate and branch inside the islets. As a consequence of this organization, the ratio of beta-cells to alpha-cells was constantly higher in the core than in the mantle part of the islets, and decreased with increasing islet diameter. This core-mantle segregation of islet cells was also observed in type 2 diabetic donors but not in cultured isolated islets. Three-dimensional analysis revealed that islet cells were in fact organized into trilaminar epithelial plates, folded with different degrees of complexity and bordered by vessels on both sides. In epithelial plates, most beta-cells were located in a central position but frequently showed cytoplasmic extensions between outlying non-beta-cells.
Conclusions: Human islets have a unique architecture allowing all endocrine cells to be adjacent to blood vessels and favoring heterologous contacts between beta- and alpha-cells, while permitting homologous contacts between beta-cells.
Figures
References
-
- Orci L, Unger RH. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet 1975;2:1243–1244 - PubMed
-
- Gannon M, Ray MK, Van Zee K, Rausa F, Costa RH, Wright CV. Persistent expression of HNF6 in islet endocrine cells causes disrupted islet architecture and loss of beta cell function. Development 2000;127:2883–2895 - PubMed
-
- Bosco D, Orci L, Meda P. Homologous but not heterologous contact increases the insulin secretion of individual pancreatic B-cells. Exp Cell Res 1989;184:72–80 - PubMed
-
- Samols E, Stagner JI. Intra-islet regulation. Am J Med 1988;85:31–35 - PubMed
-
- Samols E, Stagner JI. Islet somatostatin: microvascular, paracrine, and pulsatile regulation. Metabolism 1990;39:55–60 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

