Epigenetic repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2: implications for the biology and treatment of breast cancer
- PMID: 20185823
- PMCID: PMC2852914
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.086561
Epigenetic repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2: implications for the biology and treatment of breast cancer
Abstract
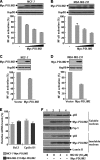
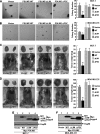
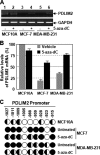
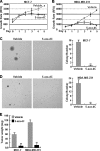
The NF-kappaB transcription factor plays a pivotal role in breast cancer progression and therapy resistance. However, the mechanisms by which the tightly regulated NF-kappaB becomes constitutively activated during breast cancer pathogenesis remain obscure. Here, we report that PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 (PDLIM2), an essential terminator of NF-kappaB activation, is repressed in both estrogen receptor-positive and estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells, suggesting one important mechanism for the constitutive activation of NF-kappaB. Indeed, PDLIM2 reexpression inhibited constitutive NF-kappaB activation and expression of NF-kappaB-targeted genes in those breast cancer cells. Importantly, PDLIM2, but not its mutants defective in NF-kappaB termination, could suppress in vitro anchorage-independent growth and in vivo tumor formation of those malignant breast cells. In addition, we have shown that PDLIM2 repression involves promoter methylation. Accordingly, treatment of the breast cancer cells with the DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine reverses the methylation of the PDLIM2 promoter, restored PDLIM2 expression, and suppressed tumorigenicities of human breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. These studies thus provide important mechanistic insights into breast cancer pathogenesis. These studies also suggest a tumor suppression function of PDLIM2 and a therapeutic strategy for breast cancer.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oncovirus Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) represses tumor suppressor PDLIM2 to persistently activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and STAT3 transcription factors for tumorigenesis and tumor maintenance.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 20;290(12):7362-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C115.637918. Epub 2015 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25681443 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation-dependent repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 in colon cancer and its role as a potential therapeutic target.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 1;70(5):1766-72. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3263. Epub 2010 Feb 9. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20145149 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I-mediated repression of PDZ-LIM domain-containing protein 2 involves DNA methylation but independent of the viral oncoprotein tax.Neoplasia. 2009 Oct;11(10):1036-41. doi: 10.1593/neo.09752. Neoplasia. 2009. PMID: 19794962 Free PMC article.
-
[PDLIM2 and Its Role in Oncogenesis--Tumor Suppressor or Oncoprote?].Klin Onkol. 2015;28 Suppl 2:2S40-6. doi: 10.14735/amko20152s40. Klin Onkol. 2015. PMID: 26374157 Review. Czech.
-
PDLIM2: Signaling pathways and functions in cancer suppression and host immunity.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Dec;1876(2):188630. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188630. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34571051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncovirus Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus (KSHV) represses tumor suppressor PDLIM2 to persistently activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and STAT3 transcription factors for tumorigenesis and tumor maintenance.J Biol Chem. 2015 Mar 20;290(12):7362-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C115.637918. Epub 2015 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25681443 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB and cancer: a paradigm of Yin-Yang.Am J Cancer Res. 2011;1(2):192-221. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Am J Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21969033 Free PMC article.
-
PDLIM2 restricts Th1 and Th17 differentiation and prevents autoimmune disease.Cell Biosci. 2012 Jun 25;2(1):23. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-2-23. Cell Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22731402 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular determinants of PDLIM2 in suppressing HTLV-I Tax-mediated tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2010 Dec 9;29(49):6499-507. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.374. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Oncogene. 2010. PMID: 20838382 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus: a model of NF-κB-associated tumorigenesis.Viruses. 2011 Jun;3(6):714-49. doi: 10.3390/v3060714. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21743832 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Hao Y., Xu J., Thun M. J. (2009) CA Cancer J. Clin. 59, 225–249 - PubMed
-
- Cao Y., Karin M. (2003) J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 8, 215–223 - PubMed
-
- Wu J. T., Kral J. G. (2005) J. Surg. Res. 123, 158–169 - PubMed
-
- Biswas D. K., Iglehart J. D. (2006) J. Cell. Physiol. 209, 645–652 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

