Natural angiogenesis inhibitor signals through Erk5 activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma)
- PMID: 20185831
- PMCID: PMC2859512
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.117374
Natural angiogenesis inhibitor signals through Erk5 activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma)
Abstract
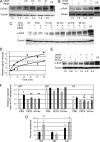
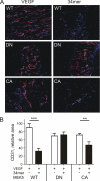
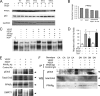
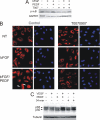
Erk-5, a member of the MAPK superfamily, has a catalytic domain similar to Erk1/2 and a unique C-terminal domain enabling binding with transcription factors. Aberrant vascularization in the Erk5-null mice suggested a link to angiogenesis. Ectopic expression of constitutively active Erk5 blocks endothelial cell morphogenesis and causes HIF1-alpha destabilization/degradation. However the mechanisms by which endogenous Erk5 regulates angiogenesis remain unknown. We show that Erk5 and its activating kinase MEK5 are the upstream mediators of the anti-angiogenic signal by the natural angiogenesis inhibitor, pigment epithelial-derived factor (PEDF). We demonstrate that Erk5 phosphorylation allows activation of PPARgamma transcription factor by displacement of SMRT co-repressor. PPARgamma, in turn is critical for NFkappaB activation, PEDF-dependent apoptosis, and anti-angiogenesis. The dominant negative MEK5 mutant and Erk5 shRNA diminished PEDF-dependent apoptosis, inhibition of the endothelial cell chemotaxis, and angiogenesis. This is the first evidence of Erk5-dependent transduction of signals by endogenous angiogenesis inhibitors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PEDF and 34-mer inhibit angiogenesis in the heart by inducing tip cells apoptosis via up-regulating PPAR-γ to increase surface FasL.Apoptosis. 2016 Jan;21(1):60-8. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1186-1. Apoptosis. 2016. PMID: 26519036
-
Cytosolic phospholipase A2-{alpha} is an early apoptotic activator in PEDF-induced endothelial cell apoptosis.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Feb;296(2):C273-84. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00432.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 17. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19091957
-
Activation of either ERK1/2 or ERK5 MAP kinase pathways can lead to disruption of the actin cytoskeleton.J Cell Sci. 2005 Apr 15;118(Pt 8):1663-71. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02308. Epub 2005 Mar 29. J Cell Sci. 2005. PMID: 15797923
-
ERK5 and its role in tumour development.Biochem Soc Trans. 2012 Feb;40(1):251-6. doi: 10.1042/BST20110663. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012. PMID: 22260700 Review.
-
Cancer cell apoptotic pathways mediated by PEDF: prospects for therapy.Trends Mol Med. 2009 Oct;15(10):461-7. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2009.08.003. Epub 2009 Sep 25. Trends Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19783213 Review.
Cited by
-
ERK5/BMK1 is a novel target of the tumor suppressor VHL: implication in clear cell renal carcinoma.Neoplasia. 2013 Jun;15(6):649-59. doi: 10.1593/neo.121896. Neoplasia. 2013. PMID: 23730213 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Protein-based Anti-metastatic Therapy with Serpins and Inter α-Trypsin Inhibitors.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2018 Jul-Aug;15(4):225-238. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20081. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2018. PMID: 29976628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanoma Cells Block PEDF Production in Fibroblasts to Induce the Tumor-Promoting Phenotype of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts.Cancer Res. 2016 Apr 15;76(8):2265-76. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-2468. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26921338 Free PMC article.
-
Pigment epithelium-derived factor and its phosphomimetic mutant induce JNK-dependent apoptosis and p38-mediated migration arrest.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 4;286(5):3540-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.151548. Epub 2010 Nov 8. J Biol Chem. 2011. Retraction in: J Biol Chem. 2017 May 26;292(21):8849. doi: 10.1074/jbc.A110.151548. PMID: 21059648 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
p53-responsive miR-194 inhibits thrombospondin-1 and promotes angiogenesis in colon cancers.Cancer Res. 2011 Dec 15;71(24):7490-501. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-1124. Epub 2011 Oct 25. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 22028325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang J., Boerm M., McCarty M., Bucana C., Fidler I. J., Zhuang Y., Su B. (2000) Nat. Genet. 24, 309–313 - PubMed
-
- Tamura K., Sudo T., Senftleben U., Dadak A. M., Johnson R., Karin M. (2000) Cell 102, 221–231 - PubMed
-
- Liu C., Shi Y., Han Z., Pan Y., Liu N., Han S., Chen Y., Lan M., Qiao T., Fan D. (2003) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 312, 780–786 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

