Enhanced anti-tumor effects of combined MDR1 RNA interference and human sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) radioiodine gene therapy using an adenoviral system in a colon cancer model
- PMID: 20186172
- PMCID: PMC2887652
- DOI: 10.1038/cgt.2010.3
Enhanced anti-tumor effects of combined MDR1 RNA interference and human sodium/iodide symporter (NIS) radioiodine gene therapy using an adenoviral system in a colon cancer model
Abstract
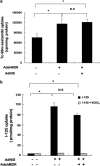
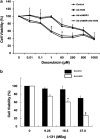
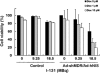
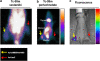
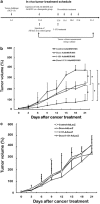
Using an adenoviral system as a delivery mediator of therapeutic gene, we investigated the therapeutic effects of the use of combined MDR1 shRNA and human NIS (hNIS) radioiodine gene therapy in a mouse colon xenograft model. In vitro uptake of Tc-99m sestamibi was increased approximately two-fold in cells infected with an adenovirus vector that expressed MDR1 shRNA (Ad-shMDR1) and I-125 uptake was 25-fold higher in cells infected with an adenovirus vector that expressed human NIS (Ad-hNIS) as compared with control cells. As compared with doxorubicin or I-131 treatment alone, the combination of doxorubicin and I-131 resulted in enhanced cytotoxicity for both Ad-shMDR1- and Ad-hNIS-infected cells, but not for control cells. In vivo uptake of Tc-99m sestamibi and Tc-99m pertechnetate was twofold and 10-fold higher for Ad-shMDR1 and Ad-hNIS-infected tumors as compared with tumors infected with a control adenovirus construct that expressed beta-galactosidase (Ad-LacZ), respectively. In mice treated with either doxorubicin or I-131 alone, there was a slight delay in tumor growth as compared to mice treated with Ad-LacZ. However, combination therapy with doxorubicin and I-131 induced further significant inhibition of tumor growth as compared with mice treated with Ad-LacZ. We have shown successful therapeutic efficacy of combined MDR shRNA and hNIS radioiodine gene therapy using an adenoviral vector system in a mouse colon cancer model. Adenovirus-mediated cancer gene therapy using MDR1 shRNA and hNIS would be a useful tool for the treatment of cancer cells expressing multi-drug resistant genes.
Figures

References
-
- Chung JK. Sodium iodide symporter: its role in nuclear medicine. J Nucl Med. 2002;43:1188–1200. - PubMed
-
- Cho JY. A transporter gene (sodium iodide symporter) for dual purposes in gene therapy: imaging and therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2002;2:393–402. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Altmann A, Mier W, Eskerski H, Leotta K, Guo L, et al. Radioiodine therapy of hepatoma using targeted transfer of the human sodium/iodide symporter gene. J Nucl Med. 2006;47:854–862. - PubMed
-
- Mandell RB, Mandell LZ, Link CJ., Jr Radioisotope concentrator gene therapy using the sodium/iodide symporter gene. Cancer Res. 1999;59:661–668. - PubMed
-
- Jeon YH, Choi Y, Kim HJ, Kim CW, Jeong JM, Lee DS, et al. Human sodium iodide symporter gene adjunctive radiotherapy to enhance the preventive effect of hMUC1 DNA vaccine. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:1593–1599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

