Influence of genetic background and tissue types on global DNA methylation patterns
- PMID: 20186319
- PMCID: PMC2826396
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009355
Influence of genetic background and tissue types on global DNA methylation patterns
Abstract
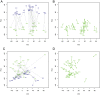
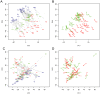
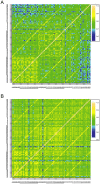
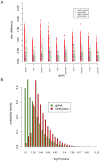
Recent studies have shown a genetic influence on gene expression variation, chromatin, and DNA methylation. However, the effects of genetic background and tissue types on DNA methylation at the genome-wide level have not been characterized extensively. To study the effect of genetic background and tissue types on global DNA methylation, we performed DNA methylation analysis using the Affymetrix 500K SNP array on tumor, adjacent normal tissue, and blood DNA from 30 patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The use of multiple tissues from 30 individuals allowed us to evaluate variation of DNA methylation states across tissues and individuals. Our results demonstrate that blood and esophageal tissues shared similar DNA methylation patterns within the same individual, suggesting an influence of genetic background on DNA methylation. Furthermore, we showed that tissue types are important contributors of DNA methylation states.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bird A, Macleod D. Reading the DNA methylation signal. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2004;69:113–118. - PubMed
-
- Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–1080. - PubMed
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:415–428. - PubMed
-
- Feinberg AP, Tycko B. The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B. Hypomethylation distinguishes genes of some human cancers from their normal counterparts. Nature. 1983;301:89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

