Postsynaptic BDNF-TrkB signaling in synapse maturation, plasticity, and disease
- PMID: 20186705
- PMCID: PMC2923204
- DOI: 10.1002/dneu.20765
Postsynaptic BDNF-TrkB signaling in synapse maturation, plasticity, and disease
Abstract
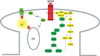
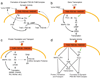
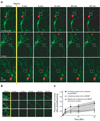
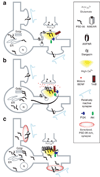
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a prototypic neurotrophin that regulates diverse developmental events from the selection of neural progenitors to the terminal dendritic differentiation and connectivity of neurons. We focus here on activity-dependent synaptic regulation by BDNF and its receptor, full length TrkB. BDNF-TrkB signaling is involved in transcription, translation, and trafficking of proteins during various phases of synaptic development and has been implicated in several forms of synaptic plasticity. These functions are carried out by a combination of the three signaling cascades triggered when BDNF binds TrkB: The mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), the phospholipase Cgamma (PLC PLCgamma), and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathways. MAPK and PI3K play crucial roles in both translation and/or trafficking of proteins induced by synaptic activity, whereas PLCgamma regulates intracellular Ca(2+) that can drive transcription via cyclic AMP and a protein kinase C. Conversely, the abnormal regulation of BDNF is implicated in various developmental and neurodegenerative diseases that perturb neural development and function. We will discuss the current state of understanding BDNF signaling in the context of synaptic development and plasticity with a focus on the postsynaptic cell and close with the evidence that basic mechanisms of BDNF function still need to be understood to effectively treat genetic disruptions of these pathways that cause devastating neurodevelopmental diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpGbinding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Barco A, Patterson S, Alarcon JM, Gromova P, Mata-Roig M, Morozov A, Kandel ER. Gene expression profiling of facilitated L-LTP in VP16-CREB mice reveals that BDNF is critical for the maintenance of LTP and its synaptic capture. Neuron. 2005;48:123–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

