Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the development of structural neuronal connectivity
- PMID: 20186709
- PMCID: PMC2893579
- DOI: 10.1002/dneu.20774
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and the development of structural neuronal connectivity
Abstract
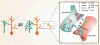
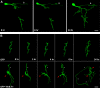
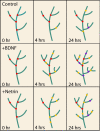
During development, neural networks are established in a highly organized manner, which persists throughout life. Neurotrophins play crucial roles in the developing nervous system. Among the neurotrophins, brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is highly conserved in gene structure and function during vertebrate evolution, and serves an important role during brain development and in synaptic plasticity. BDNF participates in the formation of appropriate synaptic connections in the brain, and disruptions in this process contribute to disorders of cognitive function. In this review, we first briefly highlight current knowledge on the expression, regulation, and secretion of BDNF. Further, we provide an overview of the possible actions of BDNF in the development of neural circuits, with an emphasis on presynaptic actions of BDNF during the structural development of central neurons.
Figures
References
-
- Alberch J, Perez-Navarro E, Canals JM. Neurotrophic factors in Huntington's disease. Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:195–229. - PubMed
-
- Alsina B, Vu T, Cohen-Cory S. Visualizing synapse formation in arborizing optic axons in vivo: dynamics and modulation by BDNF. Nat. Neurosci. 2001;4:1093–1101. - PubMed
-
- Aoki C, Wu K, Elste A, Len G, Lin S, McAuliffe G, Black IB. Localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and TrkB receptors to postsynaptic densities of adult rat cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Res. 2000;59:454–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

