Genome-wide linkage analysis of quantitative biomarker traits of osteoarthritis in a large, multigenerational extended family
- PMID: 20187133
- PMCID: PMC3684272
- DOI: 10.1002/art.27288
Genome-wide linkage analysis of quantitative biomarker traits of osteoarthritis in a large, multigenerational extended family
Abstract
Objective: The genetic contributions to the multifactorial disorder osteoarthritis (OA) have been increasingly recognized. The goal of the current study was to use OA-related biomarkers of severity and disease burden as quantitative traits to identify genetic susceptibility loci for OA.
Methods: In a large multigenerational extended family (n = 350), we measured 5 OA-related biomarkers: hyaluronan (HA), cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP), N-propeptide of type IIA collagen (PIIANP), C-propeptide of type II procollagen (CPII), and type II collagen neoepitope (C2C). Single-nucleotide polymorphism markers (n = 6,090) covering the whole genome were genotyped using the Illumina HumanLinkage-12 BeadChip. Variance components analysis, as implemented in the Sequential Oligogenic Linkage Analysis Routines, was used to estimate heritabilities of the quantitative traits and to calculate 2-point and multipoint logarithm of odds (LOD) scores using a polygenic model.
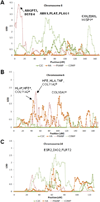
Results: After adjusting for age and sex, we found that 4 of the 5 biomarkers exhibited significant heritability (PIIANP 0.57, HA 0.49, COMP 0.43, C2C 0.30; P < or = 0.01 for all). Fourteen of the 19 loci that had multipoint LOD scores of >1.5 were near to or overlapped with previously reported OA susceptibility loci. Four of these loci were identified by more than 1 biomarker. The maximum multipoint LOD scores for the heritable quantitative biomarker traits were 4.3 for PIIANP (chromosome 8p23.2), 3.2 for COMP (chromosome 8q11.1), 2.0 for HA (chromosome 6q16.3), and 2.0 for C2C (chromosome 5q31.2).
Conclusion: Herein, we report the first evidence of genetic susceptibility loci identified by OA-related biomarkers in an extended family. Our results demonstrate that serum concentrations of PIIANP, HA, COMP, and C2C have substantial heritable components, and using these biomarkers, several genetic loci potentially contributing to the genetic diversity of OA were identified.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Biomarkers associated with clinical phenotypes of hand osteoarthritis in a large multigenerational family: the CARRIAGE family study.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008 Sep;16(9):1054-9. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.12.010. Epub 2008 Mar 4. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2008. PMID: 18291686 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of cartilage biomarkers for monitoring structural joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with anti-TNF therapy.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037447. Epub 2012 May 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22629396 Free PMC article.
-
Diurnal variation of serum and urine biomarkers in patients with radiographic knee osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Aug;54(8):2496-504. doi: 10.1002/art.21977. Arthritis Rheum. 2006. PMID: 16868970
-
Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, C-terminal cross-linking telopeptide of type II collagen, and matrix metalloproteinase-3 as biomarkers for knee and hip osteoarthritis (OA) diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019 May;27(5):726-736. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2018.10.009. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019. PMID: 30391538
-
Insights from human genetic studies into the pathways involved in osteoarthritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013 Oct;9(10):573-83. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2013.121. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23958796 Review.
Cited by
-
TSG-6 activity as a novel biomarker of progression in knee osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014 Feb;22(2):235-41. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2013.12.004. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014. PMID: 24333293 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Study Identifies Significant Epigenomic Changes in Osteoarthritic Subchondral Bone and Similarity to Overlying Cartilage.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016 Jun;68(6):1403-14. doi: 10.1002/art.39555. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26713865 Free PMC article.
-
Serum N-propeptide of collagen IIA (PIIANP) as a marker of radiographic osteoarthritis burden.PLoS One. 2017 Dec 29;12(12):e0190251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190251. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29287118 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized medicine for osteoarthritis: where are we now?Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013 Apr;5(2):67-75. doi: 10.1177/1759720X12470752. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2013. PMID: 23641258 Free PMC article.
-
IGFBP7 acts as a negative regulator of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and oestrogen deficiency-induced bone loss.Cell Prolif. 2020 Feb;53(2):e12752. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12752. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 31889368 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brooks PM. Impact of osteoarthritis on individuals and society: how much disability? Social consequences and health economic implications. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2002;14(5):573–577. - PubMed
-
- Peach CA, Carr AJ, Loughlin J. Recent advances in the genetic investigation of osteoarthritis. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11(4):186–191. - PubMed
-
- Jordan JM, Kraus VB, Hochberg MC. Genetics of osteoarthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2004;6(1):7–13. - PubMed
-
- Ikegawa S. New gene associations in osteoarthritis: what do they provide, and where are we going? Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007;19(5):429–434. - PubMed
-
- Valdes AM, Spector TD. The contribution of genes to osteoarthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2008;34(3):581–603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

