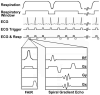
Improved arterial spin labeling after myocardial infarction in mice using cardiac and respiratory gated look-locker imaging with fuzzy C-means clustering
- PMID: 20187175
- PMCID: PMC2918386
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22280
Improved arterial spin labeling after myocardial infarction in mice using cardiac and respiratory gated look-locker imaging with fuzzy C-means clustering
Abstract
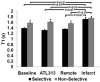
Experimental myocardial infarction (MI) in mice is an important disease model, in part due to the ability to study genetic manipulations. MRI has been used to assess cardiac structural and functional changes after MI in mice, but changes in myocardial perfusion after acute MI have not previously been examined. Arterial spin labeling noninvasively measures perfusion but is sensitive to respiratory motion and heart rate variability and is difficult to apply after acute MI in mice. To account for these factors, a cardiorespiratory-gated arterial spin labeling sequence using a fuzzy C-means algorithm to retrospectively reconstruct images was developed. Using this method, myocardial perfusion was measured in remote and infarcted regions at 1, 7, 14, and 28 days post-MI. Baseline perfusion was 4.9 +/- 0.5 mL/g min and 1 day post-MI decreased to 0.9 +/- 0.8 mL/g min in infarcted myocardium (P < 0.05 versus baseline) while remaining at 5.2 +/- 0.8 mL/g min in remote myocardium. During the subsequent 28 days, perfusion in the remote zone remained unchanged, while a partial recovery of perfusion in the infarct zone was seen. This technique, when applied to genetically engineered mice, will allow for the investigation of the roles of specific genes in myocardial perfusion during infarct healing.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures







References
-
- Carmeliet P, Collen D. Transgenic mouse models in angiogenesis and cardiovascular disease. The Journal of Pathology. 2000;190(3):387–405. - PubMed
-
- Balakumar P, Singh AP, Singh M. Rodent models of heart failure. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 2007;56(1):1. - PubMed
-
- Epstein FH. MR in mouse models of cardiac disease. NMR in Biomedicine. 2007;20(3):238–255. - PubMed
-
- Gilson WD, Epstein FH, Yang Z, Xu Y, Prasad KMR, Toufektsian MC, Laubach VE, French BA. Borderzone Contractile Dysfunction Is Transiently Attenuated and Left Ventricular Structural Remodeling Is Markedly Reduced Following Reperfused Myocardial Infarction in Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Knockout Mice. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2007;50(18):1799. - PubMed
-
- Ross AJ, Yang Z, Berr SS, Gilson WD, Petersen WC, Oshinski JN, French BA. Serial MRI evaluation of cardiac structure and function in mice after reperfused myocardial infarction. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 2002;47(6):1158–1168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

