Estimation of labeling efficiency in pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling
- PMID: 20187183
- PMCID: PMC2922009
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.22245
Estimation of labeling efficiency in pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling
Abstract
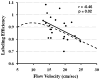
Pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling MRI is a new arterial spin labeling technique that has the potential of combining advantages of continuous arterial spin labeling and pulsed arterial spin labeling. However, unlike continuous arterial spin labeling, the labeling process of pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling is not strictly an adiabatic inversion and the efficiency of labeling may be subject specific. Here, three experiments were performed to study the labeling efficiency in pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling MRI. First, the optimal labeling position was determined empirically to be approximately 84 mm below the anterior commissure-posterior commissure line in order to achieve the highest sensitivity. Second, an experimental method was developed to utilize phase-contrast velocity MRI as a normalization factor and to estimate the labeling efficiency in vivo, which was founded to be 0.86 +/- 0.06 (n = 10, mean +/- standard deviation). Third, we compared the labeling efficiency of pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling MRI under normocapnic and hypercapnic (inhalation of 5% CO(2)) conditions and showed that a higher flow velocity in the feeding arteries resulted in a reduction in the labeling efficiency. In summary, our results suggest that labeling efficiency is a critical parameter in pseudocontinuous arterial spin labeling MRI not only in terms of achieving highest sensitivity but also in quantification of absolute cerebral blood flow in milliliters per minute per 100 g. We propose that the labeling efficiency should be estimated using phase-contrast velocity MRI on a subject-specific basis.
(c) 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Detre JA, Leigh JS, Williams DS, Koretsky AP. Perfusion imaging. Magn Reson Med. 1992;23:37–45. - PubMed
-
- Wang J, Zhang Y, Wolf RL, Roc AC, Alsop DC, Detre JA. Amplitude-modulated continuous arterial spin-labeling 3.0-T perfusion MR imaging with a single coil: feasibility study. Radiology. 2005;235:218–228. - PubMed
-
- Trampel R, Jochimsen TH, Mildner T, Norris DG, Moller HE. Efficiency of flow-driven adiabatic spin inversion under realistic experimental conditions: a computer simulation. Magn Reson Med. 2004;51:1187–1193. - PubMed
-
- O’Gorman RL, Summers PE, Zelaya FO, Williams SC, Alsop DC, Lythgoe DJ. In vivo estimation of the flow-driven adiabatic inversion efficiency for continuous arterial spin labeling: a method using phase contrast magnetic resonance angiography. Magn Reson Med. 2006;55:1291–1297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

