The role of parkin in familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 20187240
- PMCID: PMC4115293
- DOI: 10.1002/mds.22798
The role of parkin in familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease
Abstract
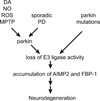
Mutations in parkin are the second most common known cause of Parkinson's disease (PD). Parkin is an ubiquitin E3 ligase that monoubiquitinates and polyubiquitinates proteins to regulate a variety of cellular processes. Loss of parkin's E3 ligase activity is thought to play a pathogenic role in both inherited and sporadic PD. Here, we review parkin biology and pathobiology and its role in the pathogenesis of PD.
Figures

References
-
- Gasser T. Genetics of Parkinson's disease. J Neurol. 2001;248(10):833–840. - PubMed
-
- Dawson TM. New animal models for Parkinson's disease. Cell. 2000;101(2):115–118. - PubMed
-
- Giasson BI, Lee VM. Parkin and the molecular pathways of Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 2001;31(6):885–888. - PubMed
-
- Lansbury PT, Brice A. Genetics of Parkinson's disease and biochemical studies of implicated gene products. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2002;12(3):299–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

