Reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase induce apoptotic death of U937 cells in response to Naja nigricollis toxin-gamma
- PMID: 20187293
- PMCID: PMC6512387
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00473.x
Reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase induce apoptotic death of U937 cells in response to Naja nigricollis toxin-gamma
Abstract
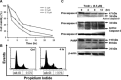
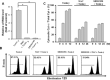
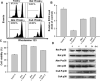
The aim of the present study is to elucidate the signalling components related to Naja nigricollis toxin--induced apoptosis in human leukaemia U937 cells. It was found that toxin--induced apoptotic cell death was attributed mainly to activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsim). Subsequent modulation of Bcl-2 family member and cytochrome c release accompanied with activation of caspase-9 and -3 were involved in the death of U937 cells. SB202190 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) and N-acetylcysteine (antioxidant) significantly attenuated toxin--induced cell death and loss of deltapsim, and completely abolished the production of ROS. In contrast to N-acetylcysteine, degradation of Bcl-2/Bcl-XL and mitochondrial localization of Bax were notably decreased by SB202190. Inhibitors of electron transport (rotenone and antimycin A) or inhibitor of mitochondrial permeability transition pore (cyclosporine A) reduced the effect of toxin- on ROS generation, loss of deltapsim and cytochrome c release. Noticeably, pre-treatment with N-acetylcysteine or rotenone eliminated markedly ROS accompanied with reduction in p38 MAPK activation. Taken together, these results suggest that the cytotoxicity of toxin- is initiated by p38-MAPK-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction followed by ROS production and activation of caspases, and that ROS further augments p38 MAPK activation and mitochondrial alteration.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Naja nigricollis CMS-9 enhances the mitochondria-mediated death pathway in adaphostin-treated human leukaemia U937 cells.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011 Nov;38(11):755-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05585.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21824174
-
Involvement of mitochondrial alteration and reactive oxygen species generation in Taiwan cobra cardiotoxin-induced apoptotic death of human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells.Toxicon. 2008 Aug 1;52(2):361-8. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2008.06.013. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Toxicon. 2008. PMID: 18619991
-
Involvement of p38 MAPK- and JNK-modulated expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in Naja nigricollis CMS-9-induced apoptosis of human leukemia K562 cells.Toxicon. 2010 Jun 15;55(7):1306-16. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2010.01.024. Epub 2010 Feb 6. Toxicon. 2010. PMID: 20144638
-
ROS-mediated p38alpha MAPK activation and ERK inactivation responsible for upregulation of Fas and FasL and autocrine Fas-mediated cell death in Taiwan cobra phospholipase A(2)-treated U937 cells.J Cell Physiol. 2009 Jun;219(3):642-51. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21713. J Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19180563
-
Calcium-stimulated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation elicits Bcl-xL downregulation and Bak upregulation in notexin-treated human neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Jan;222(1):177-86. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21934. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19780038
Cited by
-
Naja atra Cardiotoxin 3 Elicits Autophagy and Apoptosis in U937 Human Leukemia Cells through the Ca2+/PP2A/AMPK Axis.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Sep 12;11(9):527. doi: 10.3390/toxins11090527. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547294 Free PMC article.
-
Propensity of crocin to offset Vipera russelli venom induced oxidative stress mediated neutrophil apoptosis: a biochemical insight.Cytotechnology. 2016 Jan;68(1):73-85. doi: 10.1007/s10616-014-9752-x. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Cytotechnology. 2016. PMID: 25149285 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of ADAM17-mediated Lyn/Akt pathways induces apoptosis of human leukemia U937 cells: Bungarus multicinctus protease inhibitor-like protein-1 uncovers the cytotoxic mechanism.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 1;285(40):30506-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.156257. Epub 2010 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20679348 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviation of viper venom induced platelet apoptosis by crocin (Crocus sativus): implications for thrombocytopenia in viper bites.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2013 Nov;36(4):424-32. doi: 10.1007/s11239-013-0888-x. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2013. PMID: 23412973 Clinical Trial.
-
Juglone induces apoptosis of tumor stem-like cells through ROS-p38 pathway in glioblastoma.BMC Neurol. 2017 Apr 7;17(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12883-017-0843-0. BMC Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28388894 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson N, Melton B. Leukocytosis: basics of clinical assessment. Am Fam Physician . 2000; 62: 2053–60. - PubMed
-
- Schneider E, Cowan KH, Bader H, et al . Increased expression of the multidrug resistance‐associated protein gene in relapsed acute leukemia. Blood . 1995; 85: 186–93. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Dallaporta B, Resche‐Rigon M. The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu Rev Physiol . 1998; 60: 619–42. - PubMed
-
- Del Poeta G, Venditti A, Del Principe MI, et al . Amount of spontaneous apoptosis detected by Bax/Bcl‐2 ratio predicts outcome in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood . 2003; 101: 2125–31. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZY. Ham‐Wasserman lecture: treatment of acute leukemia by inducing differentiation and apoptosis. Hematology . 2003; 1: 1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

