Reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase induce apoptotic death of U937 cells in response to Naja nigricollis toxin-gamma
- PMID: 20187293
- PMCID: PMC6512387
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00473.x
Reactive oxygen species and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase induce apoptotic death of U937 cells in response to Naja nigricollis toxin-gamma
Abstract
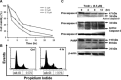
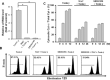
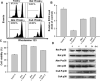
The aim of the present study is to elucidate the signalling components related to Naja nigricollis toxin--induced apoptosis in human leukaemia U937 cells. It was found that toxin--induced apoptotic cell death was attributed mainly to activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsim). Subsequent modulation of Bcl-2 family member and cytochrome c release accompanied with activation of caspase-9 and -3 were involved in the death of U937 cells. SB202190 (p38 MAPK inhibitor) and N-acetylcysteine (antioxidant) significantly attenuated toxin--induced cell death and loss of deltapsim, and completely abolished the production of ROS. In contrast to N-acetylcysteine, degradation of Bcl-2/Bcl-XL and mitochondrial localization of Bax were notably decreased by SB202190. Inhibitors of electron transport (rotenone and antimycin A) or inhibitor of mitochondrial permeability transition pore (cyclosporine A) reduced the effect of toxin- on ROS generation, loss of deltapsim and cytochrome c release. Noticeably, pre-treatment with N-acetylcysteine or rotenone eliminated markedly ROS accompanied with reduction in p38 MAPK activation. Taken together, these results suggest that the cytotoxicity of toxin- is initiated by p38-MAPK-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction followed by ROS production and activation of caspases, and that ROS further augments p38 MAPK activation and mitochondrial alteration.
Figures







References
-
- Abramson N, Melton B. Leukocytosis: basics of clinical assessment. Am Fam Physician . 2000; 62: 2053–60. - PubMed
-
- Schneider E, Cowan KH, Bader H, et al . Increased expression of the multidrug resistance‐associated protein gene in relapsed acute leukemia. Blood . 1995; 85: 186–93. - PubMed
-
- Kroemer G, Dallaporta B, Resche‐Rigon M. The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu Rev Physiol . 1998; 60: 619–42. - PubMed
-
- Del Poeta G, Venditti A, Del Principe MI, et al . Amount of spontaneous apoptosis detected by Bax/Bcl‐2 ratio predicts outcome in acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood . 2003; 101: 2125–31. - PubMed
-
- Wang ZY. Ham‐Wasserman lecture: treatment of acute leukemia by inducing differentiation and apoptosis. Hematology . 2003; 1: 1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

