Improved cancer therapy and molecular imaging with multivalent, multispecific antibodies
- PMID: 20187791
- PMCID: PMC2883519
- DOI: 10.1089/cbr.2009.0690
Improved cancer therapy and molecular imaging with multivalent, multispecific antibodies
Abstract
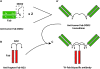
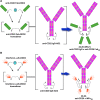
Antibodies are highly versatile proteins with the ability to be used to target diverse compounds, such as radionuclides for imaging and therapy, or drugs and toxins for therapy, but also can be used unconjugated to elicit therapeutically beneficial responses, usually with minimal toxicity. This update describes a new procedure for forming multivalent and/or multispecific proteins, known as the dock-and-lock (DNL) technique. Developed as a procedure for preparing bispecific antibodies capable of binding divalently to a tumor antigen and monovalently to a radiolabeled hapten-peptide for pretargeted imaging and therapy, this methodology has the flexibility to create a number of other biologic agents of therapeutic interest. A variety of constructs, based on anti-CD20 and CD22 antibodies, have been made, with results showing that multispecific antibodies have very different properties from the respective parental monospecific antibodies. The technique is not restricted to antibody combination, but other biologics, such as interferon-alpha2b, have been prepared. These types of constructs not only allow small biologics to be sustained in the blood longer, but also to be selectively targeted. Thus, DNL technology is a highly flexible platform that can be used to prepare many different types of agents that could further improve cancer detection and therapy.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Optimization of multivalent bispecific antibodies and immunocytokines with improved in vivo properties.Bioconjug Chem. 2013 Jan 16;24(1):63-71. doi: 10.1021/bc300488f. Epub 2012 Dec 21. Bioconjug Chem. 2013. PMID: 23116517
-
Emerging new therapeutic antibody derivatives for cancer treatment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Feb 7;7(1):39. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00868-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35132063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bispecific Antibodies and Antibody-Drug Conjugates for Cancer Therapy: Technological Considerations.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 26;10(3):360. doi: 10.3390/biom10030360. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32111076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Update on novel monoclonal antibodies and immunoconjugates for the treatment of lymphoproliferative disorders.Future Oncol. 2011 Aug;7(8):963-79. doi: 10.2217/fon.11.79. Future Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21823892 Review.
-
Pretargeted versus directly targeted radioimmunotherapy combined with anti-CD20 antibody consolidation therapy of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.J Nucl Med. 2009 Mar;50(3):444-53. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.058602. Epub 2009 Feb 17. J Nucl Med. 2009. PMID: 19223402
Cited by
-
Pretargeted molecular imaging and radioimmunotherapy.Theranostics. 2012;2(5):523-40. doi: 10.7150/thno.3582. Epub 2012 May 17. Theranostics. 2012. PMID: 22737190 Free PMC article.
-
Current progress in innovative engineered antibodies.Protein Cell. 2018 Jan;9(1):86-120. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0457-8. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Protein Cell. 2018. PMID: 28822103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical parameters for design and development of multivalent nanoconstructs: recent trends.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022 Oct;12(10):2335-2358. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-01103-4. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35013982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospective of 68Ga Radionuclide Contribution to the Development of Imaging Agents for Infection and Inflammation.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018 Jan 4;2018:9713691. doi: 10.1155/2018/9713691. eCollection 2018. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29531507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioorthogonal chemistry: implications for pretargeted nuclear (PET/SPECT) imaging and therapy.Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014 Mar 20;4(2):96-113. eCollection 2014. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014. PMID: 24753979 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pressman D. The zone of localization of antibodies: The specific localization of antibodies to rat kidney. Cancer. 1949;2:697. - PubMed
-
- Pressman D. Korngold L. The in vivo localization of anti–Wagner-osteogenic-sarcoma antibodies. Cancer. 1953;6:619. - PubMed
-
- Bale WF. Spar IL. Goodland RL. Experimental radiation therapy of tumors with I-131-carrying antibodies to fibrin. Cancer Res. 1960;20:1488. - PubMed
-
- Goldenberg DM. Hansen HJ. Carcinoembryonic antigen present in human colonic neoplasms serially propagated in hamsters. Science. 1972;175:1117. - PubMed
-
- Primus FJ. Wang RH. Goldenberg DM, et al. Localization of human GW-39 tumors in hamsters by radiolabeled heterospecific antibody to carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res. 1973;33:2977. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

