Platelet monoamine oxidase activity predicts alcohol sensitivity and voluntary alcohol intake in rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 20187848
- PMCID: PMC2853354
- DOI: 10.3109/03009731003605813
Platelet monoamine oxidase activity predicts alcohol sensitivity and voluntary alcohol intake in rhesus monkeys
Abstract
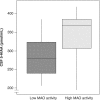
Platelet monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) has been proposed to be a biological marker for the properties of monoamine systems, with low activity being associated with vulnerability for high scores on personality traits such as sensation seeking, monotony avoidance, and impulsiveness, as well as for vulnerability for alcoholism. In the present study, platelet MAO-B activity was analysed in 78 rhesus macaques, and its relation to voluntary alcohol intake and behaviours after intravenous alcohol administration was observed. Monkeys with low platelet MAO-B activity had low levels of 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid in cerebrospinal fluid and showed excessive aggression after alcohol administration. A novel finding was that animals with low platelet MAO-B activity showed less intoxication following alcohol administration. As we have shown previously, they also voluntarily consumed more alcohol. We here replicate results from studies on both humans and non-human primates, showing the utility of platelet MAO as a marker for risk behaviours and alcohol abuse. Furthermore, we link platelet MAO activity to alcohol sensitivity.
Figures
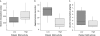
Similar articles
-
Platelet monoamine oxidase activity in a nonhuman primate model of type 2 excessive alcohol consumption.Am J Psychiatry. 2002 Dec;159(12):2107. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.12.2107. Am J Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 12450967
-
Platelet monoamine oxidase, personality and alcoholism: the rise, fall and resurrection.Neurotoxicology. 2004 Jan;25(1-2):79-89. doi: 10.1016/S0161-813X(03)00115-3. Neurotoxicology. 2004. PMID: 14697883 Review.
-
Monoamine oxidase-B activity in alcohol withdrawal of smokers: is there any relationship with aggressiveness?Alcohol Alcohol. 2002 May-Jun;37(3):272-6. doi: 10.1093/alcalc/37.3.272. Alcohol Alcohol. 2002. PMID: 12003917
-
Smoking only explains part of the associations between platelet monoamine oxidase activity and personality.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2002 May;109(5-6):963-75. doi: 10.1007/s007020200079. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2002. PMID: 12111482 Review.
-
Clinical characteristics of female alcoholics with low platelet monoamine oxidase activity.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1990 Apr;14(2):227-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1990.tb00477.x. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1990. PMID: 1693477
Cited by
-
Does patchouli oil change blood platelet monoamine oxidase-A activity of adult mammals?J Physiol Sci. 2018 May;68(3):281-291. doi: 10.1007/s12576-017-0534-z. Epub 2017 Apr 1. J Physiol Sci. 2018. PMID: 28365907 Free PMC article.
-
The biometric measurement of alcohol consumption.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 Feb;36(2):332-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01605.x. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 21895709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen K, Wu HF, Shih JC. The deduced amino acid sequences of human platelet and frontal cortex monoamine oxidase B are identical. J Neurochem. 1993;61:187–90. - PubMed
-
- Gottfries CG, Oreland L, Wiberg A, Winblad B. Lowered monoamine oxidase activity in brains from alcoholic suicides. J Neurochem. 1975;25:667–73. - PubMed
-
- Buchsbaum MS, Coursey RD, Murphy DL. The biochemical high-risk paradigm: behavioral and familial correlates of low platelet monoamine oxidase activity. Science. 1976;194:339–41. - PubMed
-
- Wiberg A, Gottfries CG, Oreland L. Low platelet monoamine oxidase activity in human alcoholics. Med Biol. 1977;55:181–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
