The glucocorticoid receptor in the distal nephron is not necessary for the development or maintenance of dexamethasone-induced hypertension
- PMID: 20188070
- PMCID: PMC2946623
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.123
The glucocorticoid receptor in the distal nephron is not necessary for the development or maintenance of dexamethasone-induced hypertension
Abstract
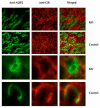
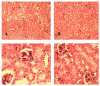
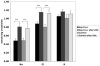
Glucocorticoids are used as a treatment for a variety of conditions and hypertension is a well-recognized side effect of their use. The mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced hypertension is incompletely understood and has traditionally been attributed to promiscuous activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor by cortisol. Multiple lines of evidence, however, point to the glucocorticoid receptor as an important mediator as well. We have developed a mouse model of glucocorticoid-induced hypertension, which is dependent on the glucocorticoid receptor. To determine the site(s) of glucocorticoid receptor action relevant to the development of hypertension, we studied glucocorticoid-induced hypertension in a mouse with a tissue-specific knockout of the glucocorticoid receptor in the distal nephron. Although knockout mice had similar body weight, nephron number and renal histology compared to littermate controls, their baseline blood pressure was mildly elevated. Nevertheless, distal nephron glucocorticoid receptor knockout mice and controls had a similar hypertensive response to dexamethasone. Urinary excretion of electrolytes, both before and after administration of glucocorticoid was also indistinguishable between the two groups. We conclude that the glucocorticoid receptor in the distal nephron is not necessary for the development or maintenance of dexamethasone-induced hypertension in our model.
2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
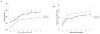
References
-
- Mangos GJ, Whitworth JA, Williamson PM, Kelly JJ. Glucocorticoids and the kidney. Nephrology (Carlton) 2003;8:267–73. - PubMed
-
- Muller OG, Parnova RG, Centeno G, Rossier BC, Firsov D, Horisberger JD. Mineralocorticoid effects in the kidney: correlation between alphaENaC, GILZ, and Sgk-1 mRNA expression and urinary excretion of Na+ and K+ J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003;14:1107–15. - PubMed
-
- Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Fejes-Toth G. Glucocorticoid receptors mediate mineralocorticoid-like effects in cultured collecting duct cells. Am J Physiol. 1990;259:F672–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

