Combination of sildenafil and simvastatin ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats
- PMID: 20188205
- PMCID: PMC3108059
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pupt.2010.02.003
Combination of sildenafil and simvastatin ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats
Abstract
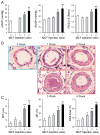
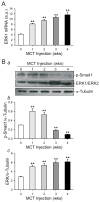
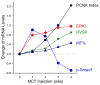
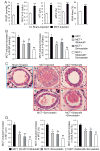
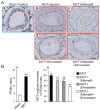
Sildenafil, a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, and simvastatin, a cholesterol lowering drug, both have therapeutic effects on PAH; however, the combination of these drugs has not been tested in the treatment of PAH. The purpose of this study was to determine whether the combination of sildenafil and simvastatin is superior to each drug alone in the prevention of MCT-induced PAH. Phosphorylated Smad levels were decreased in lung tissue in MCT-injected rats, whereas ERK protein levels were increased. This indicates a possible role for an increase in mitogenic ERK activity in addition to decreased proapoptotic Smad signaling in the MCT model of PAH. Combination sildenafil and simvastatin treatment prevented the MCT-induced increases in right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), exerted an anti-proliferative effect on pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMC). Our results indicate that combination therapy with sildenafil and simvastatin attenuated the development of pulmonary hypertension more than either treatment alone.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tadalafil, a long-acting inhibitor of PDE5, improves pulmonary hemodynamics and survival rate of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary artery hypertension in rats.J Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Nov;111(3):235-43. doi: 10.1254/jphs.09110fp. Epub 2009 Oct 31. J Pharmacol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19881228
-
Combination therapy with fasudil and sildenafil ameliorates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension and survival in rats.Circ J. 2014;78(4):967-76. doi: 10.1253/circj.cj-13-1174. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Circ J. 2014. PMID: 24553194
-
Simvastatin and sildenafil combine to attenuate pulmonary hypertension.Eur Respir J. 2009 Oct;34(4):948-57. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00143508. Eur Respir J. 2009. PMID: 19797670
-
Sildenafil for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension in pediatric patients.Pediatr Cardiol. 2009 Oct;30(7):871-82. doi: 10.1007/s00246-009-9523-1. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Pediatr Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19705181 Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors in pulmonary arterial hypertension.Adv Ther. 2009 Sep;26(9):813-25. doi: 10.1007/s12325-009-0064-z. Epub 2009 Sep 19. Adv Ther. 2009. PMID: 19768639 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel Therapeutic Approach in the Treatment of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Allium ursinum Liophylisate Alleviates Symptoms Comparably to Sildenafil.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 4;18(7):1436. doi: 10.3390/ijms18071436. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28677661 Free PMC article.
-
Are statins beneficial for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension?Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2017 Dec 11;3(4):213-220. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2017.10.001. eCollection 2017 Dec. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 29354804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simvastatin protects heart function and myocardial energy metabolism in pulmonary arterial hypertension induced right heart failure.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021 Feb;53(1):1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10863-020-09867-z. Epub 2021 Jan 4. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2021. PMID: 33394312
-
Matrix metalloproteinases are possible targets in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension: investigation of anti-remodeling effects of alagebrium and everolimus.Anatol J Cardiol. 2017 Jan;17(1):8-17. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2016.6891. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Anatol J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27182612 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin, sildenafil and their combination in monocrotaline induced pulmonary arterial hypertension.Korean Circ J. 2010 Dec;40(12):659-64. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2010.40.12.659. Epub 2010 Dec 31. Korean Circ J. 2010. PMID: 21267389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farber HW, Loscalzo J. Pulmonary arterial hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(16):1655–65. - PubMed
-
- Lane KB, Machado RD, Pauciulo MW, Thomson JR, Phillips JA, 3rd, Loyd JE, Nichols WC, Trembath RC. Heterozygous germline mutations in BMPR2, encoding a TGF-beta receptor, cause familial primary pulmonary hypertension. Nat Genet. 2000;26(1):81–4. - PubMed
-
- Yu PB, Beppu H, Kawai N, Li E, Bloch KD. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) type II receptor deletion reveals BMP ligand-specific gain of signaling in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(26):24443–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

