Systemic immunization with CCL27/CTACK modulates immune responses at mucosal sites in mice and macaques
- PMID: 20188250
- PMCID: PMC4396814
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.10.095
Systemic immunization with CCL27/CTACK modulates immune responses at mucosal sites in mice and macaques
Abstract
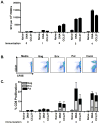
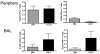
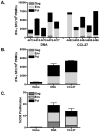
Plasmid DNA is a promising vaccine platform that has been shown to be safe and able to be administered repeatedly without vector interference. Enhancing the potency of DNA vaccination through co-delivery of molecular adjuvants is one strategy currently under investigation. Here we describe the use of the novel chemokine adjuvant CCL27/CTACK to enhance immune responses to an HIV-1 or SIV antigen in mice and rhesus macaques. CCL27 has been shown to play a role in inflammatory responses through chemotaxis of CCR10+ cells, and we hypothesized that CCL27 may modulate adaptive immune responses. Immunizations in mice with HIV-1gag/CCL27 enhanced immune responses both at peripheral and, surprisingly, at mucosal sites. To confirm these findings in a large-animal model, we created optimized CCL27 and SIV antigenic plasmid constructs for rhesus macaques. 10 macaques (n=5/group) were immunized intramuscularly with 1mg/construct of antigenic plasmids+/-CCL27 with electroporation. We observed significant IFN-gamma secretion and CD8+ T-cell proliferation in peripheral blood. Interestingly, CCL27 co-immunized macaques exhibited a trend toward greater effector CD4+ T cells in the bronchiolar lavage (BAL). CCL27 co-delivery also elicited greater antigen-specific IgA at unique sites including BAL and fecal samples but not in the periphery. Future studies incorporating CCL27 as an adjuvant in vaccine or therapy models where eliciting immune responses in the lung are warranted.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


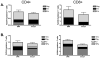

References
-
- Hokey DA, Weiner DB. DNA vaccines for HIV: challenges and opportunities. Springer seminars in immunopathology. 2006 Nov;28(3):267–79. - PubMed
-
- Gao F, Li Y, Decker JM, Peyerl FW, Bibollet-Ruche F, Rodenburg CM, et al. Codon usage optimization of HIV type 1 subtype C gag, pol, env, and nef genes: in vitro expression and immune responses in DNA-vaccinated mice. AIDS research and human retroviruses. 2003 Sep;19(9):817–23. - PubMed
-
- Leifert JA, Rodriguez-Carreno MP, Rodriguez F, Whitton JL. Targeting plasmid-encoded proteins to the antigen presentation pathways. Immunological reviews. 2004 Jun;199:40–53. - PubMed
-
- Fuller DH, Loudon P, Schmaljohn C. Preclinical and clinical progress of particle-mediated DNA vaccines for infectious diseases. Methods (San Diego, Calif. 2006 Sep;40(1):86–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

