Catastrophizing delays the analgesic effect of distraction
- PMID: 20188470
- PMCID: PMC2860661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.11.012
Catastrophizing delays the analgesic effect of distraction
Abstract
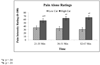
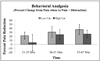
Behavioral analgesic techniques such as distraction reduce pain in both clinical and experimental settings. Individuals differ in the magnitude of distraction-induced analgesia, and additional study is needed to identify the factors that influence the pain relieving effects of distraction. Catastrophizing, a set of negative emotional and cognitive processes, is widely recognized to be associated with increased reports of pain. We sought to evaluate the relationship between catastrophizing and distraction analgesia. Healthy participants completed three sessions in a randomized order. In one session (Pain Alone), pain was induced by topical application of a 10% capsaicin cream and simultaneous administration of a tonic heat stimulus. In another session (Pain+Distraction), identical capsaicin+heat application procedures were followed, but subjects played video games that required a high level of attention. During both sessions, verbal ratings of pain were obtained and participants rated their degree of catastrophizing. During the other session (Distraction Alone) subjects played the video games in the absence of any pain stimulus. Pain was rated significantly lower during the distraction session compared to the "Pain Alone" session. In addition, high catastrophizers rated pain significantly higher regardless of whether the subjects were distracted. Catastrophizing did not influence the overall degree of distraction analgesia; however, early in the session high catastrophizers had little distraction analgesia, though later in the session low and high catastrophizers rated pain similarly. These results suggest that both distraction and catastrophizing have substantial effects on experimental pain in normal subjects and these variables interact as a function of time.
Copyright 2009 International Association for the Study of Pain. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Catastrophizing and pain coping: moving forward.Pain. 2010 May;149(2):165-166. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.02.030. Epub 2010 Mar 7. Pain. 2010. PMID: 20211526 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anderson WS, Sheth RN, Bencherif B, Frost JJ, Campbell JN. Naloxone increases pain induced by topical capsaicin in healthy human volunteers. Pain. 2002;99:207–216. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A, Cioffi D, Taylor CB, Brouillard ME. Perceived self-efficacy in coping with cognitive stressors and opioid activation. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1988;55:479–488. - PubMed
-
- Bantick SJ, Wise RG, Ploghaus A, Clare S, Smith SM, Tracey I. Imaging how attention modulates pain in humans using functional MRI. Brain. 2002;125:310–319. - PubMed
-
- Bencherif B, Fuchs PN, Sheth R, Dannals RF, Campbell JN, Frost JJ. Pain activation of human supraspinal opioid pathways as demonstrated by [11C]-carfentanil and positron emission tomography (PET) Pain. 2002;99:589–598. - PubMed
-
- Brooks JC, Nurmikko TJ, Bimson WE, Singh KD, Roberts N. fMRI of thermal pain: effects of stimulus laterality and attention. Neuroimage. 2002;15:293–301. - PubMed

