Discovery of dual inhibitors of the immune cell PI3Ks p110delta and p110gamma: a prototype for new anti-inflammatory drugs
- PMID: 20189103
- PMCID: PMC2858875
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.01.010
Discovery of dual inhibitors of the immune cell PI3Ks p110delta and p110gamma: a prototype for new anti-inflammatory drugs
Abstract
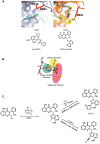
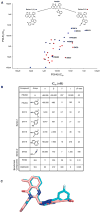
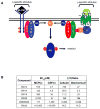
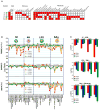
PI3Kdelta and PI3Kgamma regulate immune cell signaling, while the related PI3Kalpha and PI3Kbeta regulate cell survival and metabolism. Selective inhibitors of PI3Kdelta/gamma represent a potential class of anti-inflammatory agents lacking the antiproliferative effects associated with PI3Kalpha/beta inhibition. Here we report the discovery of PI3Kdelta/gamma inhibitors that display up to 1000-fold selectivity over PI3Kalpha/beta and evaluate these compounds in a high-content inflammation assay using mixtures of primary human cells. We find selective inhibition of only PI3Kdelta is weakly anti-inflammatory, but PI3Kdelta/gamma inhibitors show superior inflammatory marker suppression through suppression of lipopolysaccharide-induced TNFalpha production and T cell activation. Moreover, PI3Kdelta/gamma inhibition yields an anti-inflammatory signature distinct from pan-PI3K inhibition and known anti-inflammatory drugs, yet bears striking similarities to glucocorticoid receptor agonists. These results highlight the potential of selectively designing drugs that target kinases with shared biological function.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of novel quinazolinone derivatives as high potent and selective PI3Kδ and PI3Kδ/γ inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 May 10;151:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.068. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29601991
-
Isoform selective phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma and delta inhibitors and their therapeutic potential.Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008 Jan;2(1):1-10. doi: 10.2174/187221308783399270. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008. PMID: 19075988 Review.
-
Differential regulation of cytokine production by PI3Kdelta in human monocytes upon acute and chronic inflammatory conditions.Mol Immunol. 2008 Jul;45(12):3419-27. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2008.04.001. Epub 2008 May 9. Mol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18471882
-
Role of PI3Kdelta and PI3Kgamma in inflammatory arthritis and tissue localization of neutrophils.Eur J Immunol. 2008 May;38(5):1215-24. doi: 10.1002/eji.200838266. Eur J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18412166 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K signalling in inflammation.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1851(6):882-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.12.006. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25514767 Review.
Cited by
-
Herbal Formula SS-1 Increases Tear Secretion for Sjögren's Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 24;12:645437. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.645437. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34630072 Free PMC article.
-
[Mechanism of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway for mediating anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant effects of chrysin: a protein microarray-based study].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Oct 20;41(10):1554-1561. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.10.15. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34755672 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Discovery of Pyrazolopyrimidine Derivatives as Novel Dual Inhibitors of BTK and PI3Kδ.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016 Oct 28;7(12):1161-1166. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.6b00356. eCollection 2016 Dec 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2016. PMID: 27994757 Free PMC article.
-
Two birds with one stone: dual p110δ and p110γ inhibition.Chem Biol. 2013 Nov 21;20(11):1309-10. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2013.11.002. Chem Biol. 2013. PMID: 24267274 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-atherogenic cytokine interleukin-33 inhibits the expression of a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-1, -4 and -5 in human macrophages: Requirement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase and phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling pathways.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jan;46:113-23. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.008. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24275094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali K, Bilancio A, Thomas M, Pearce W, Gilfillan A, Tkaczyk C, Kuehn N, Gray A, Giddings J, Peskett E, et al. Essential role for the p110 delta phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the allergic response. Nature. 2004;431:1007–1011. - PubMed
-
- Backhouse C, Engler C, English J. Naproxen Sodium and Indomethacin in Acute Musculoskeletal Disorders. Rheumatol Rehabil. 1980;19:113–119. - PubMed
-
- Berg E, Kunkel E, Hytopoulos E, Plavec I. Characterization of compound mechanisms and secondary activities by BioMAP analysis. Journal of Pharmacological and Toxicological Methods. 2006;53:67–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

