Molecular mechanisms of hepcidin regulation: implications for the anemia of CKD
- PMID: 20189278
- PMCID: PMC2905036
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2009.12.030
Molecular mechanisms of hepcidin regulation: implications for the anemia of CKD
Abstract
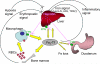
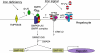
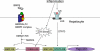
Anemia is prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and is associated with lower quality of life and higher risk of adverse outcomes, including cardiovascular disease and death. Anemia management in patients with CKD currently revolves around the use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and supplemental iron. However, many patients do not respond adequately and/or require high doses of these medications. Furthermore, recent clinical trials have shown that targeting higher hemoglobin levels with conventional therapies leads to increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, particularly when higher doses of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents are used and in patients who are poorly responsive to therapy. One explanation for the poor response to conventional therapies in some patients is that these treatments do not fully address the underlying cause of the anemia. In many patients with CKD, as with patients with other chronic inflammatory diseases, poor absorption of dietary iron and the inability to use the body's iron stores contribute to the anemia. Recent research suggests that these abnormalities in iron balance may be caused by increased levels of the key iron regulatory hormone hepcidin. This article reviews the pathogenesis of anemia in CKD, the role and regulation of hepcidin in systemic iron homeostasis and the anemia of CKD, and the potential diagnostic and therapeutic implications of these findings.
Copyright 2010 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- National Kidney Foundation KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47(5)(suppl 3):S1–S145. - PubMed
-
- Besarab A, Bolton WK, Browne JK, et al. The effects of normal as compared with low hematocrit values in patients with cardiac disease who are receiving hemodialysis and epoetin. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(9):584–90. - PubMed
-
- Singh AK, Szczech L, Tang KL, et al. Correction of anemia with epoetin alfa in chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(20):2085–2098. - PubMed
-
- Weiss G, Goodnough LT. Anemia of chronic disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):1011–1023. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

