T2 Family ribonucleases: ancient enzymes with diverse roles
- PMID: 20189811
- PMCID: PMC2888479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2010.02.002
T2 Family ribonucleases: ancient enzymes with diverse roles
Abstract
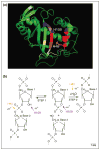
Ribonucleases of the T2 family are found in the genomes of protozoans, plants, bacteria, animals and viruses. A broad range of biological roles for these ribonucleases have been suggested, including scavenging of nucleic acids, degradation of self-RNA, serving as extra- or intracellular cytotoxins, and modulating host immune responses. Recently, RNaseT2 family members have been implicated in human pathologies such as cancer and parasitic diseases. Interestingly, certain functions of RNaseT2 family members are independent of their nuclease activity, suggesting that these proteins have additional functions. Moreover, humans lacking RNASET2 manifest a defect in neurological development, perhaps due to aberrant control of the immune system. We review the basic structure and function of RNaseT2 family members and their biological roles.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Deshpande RA, Shankar V. Ribonucleases from T2 family. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2002;28:79–122. - PubMed
-
- Irie M. Structure-function relationships of acid ribonucleases: lysosomal, vacuolar, and periplasmic enzymes. Pharmacol Ther. 1999;81:77–89. - PubMed
-
- Goldraij A, et al. Compartmentalization of S-RNase and HT-B degradation in self-incompatible Nicotiana. Nature. 2006;439:805–810. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

