Production of recombinant proteins from protozoan parasites
- PMID: 20189877
- PMCID: PMC2862126
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2010.02.004
Production of recombinant proteins from protozoan parasites
Abstract
Although the past decade has witnessed sequencing from an increasing number of parasites, modern high-throughput DNA sequencing technologies have the potential to generate complete genome sequences at even higher rates. Along with the discovery of genes that might constitute potential targets for chemotherapy or vaccination, the need for novel protein expression platforms has become a pressing matter. In addition to reviewing the advantages and limitations of the currently available and emerging expression systems, we discuss novel approaches that could overcome current limitations, including the 'pseudoparasite' concept, an expression platform in which the choice of the surrogate organism is based on its phylogenetic affinity to the target parasite, while taking advantage of the whole engineered organism as a vaccination adjuvant.
Figures
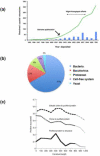

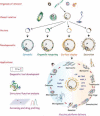
References
-
- de Azevedo WF, Jr., Soares MB. Selection of targets for drug development against protozoan parasites. Curr. Drug Targets. 2009;10:193–201. - PubMed
-
- Coombs A. The sequencing shakeup. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008;26:1109–1112. - PubMed
-
- Seitzer U, et al. Evaluation of Theileria annulata recombinant immunodominant proteins for the development of ELISA. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2008;55:244–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

